Return Values
If this was math class, the definition of a mathimatical function might be, “… a function is a relation between sets that associates to every element of a first set exactly one element of the second set,” which is a fancy way to say that if you put in a particular number into the function you get one and only one number out and it will always be the same value. The key is that you actually get something back. In computer science it is also common for functions to give you something back and we normally call this a return value or statement.
We have already seen many built in functions that have a return value, like the square root function:
Code for Function with a Return Value
// square root function someVariable = sqrt(someNumber);
// square root function someVariable = sqrt(someNumber);
// square root function someVariable = sqrt(someNumber);
// square root function someVariable = math.Sqrt(someNumber);
// square root function someVariable = sqrt(someNumber);
// square root function someVariable = sqrt(someNumber);
# square root function some_variable = math.sqrt(some_number)
You will notice that the function is now on the right hand side of an assignment statement and the calculated value is being placed right into another variable. To allow this ability, we normally use the reserved word “return” to pass the value back. In many programming languages, in the definition of the function you must specify what type of variable will be returned. This way the IDE can confirm that the same types are being passed back and placed into a variable of the same type. This way the language remains type safe.
float calculateArea(int radius) {
// this function calculates the area of circle
// process
float area = M_PI * radius ** 2;
return area;
}
float calculateArea(int radius) {
// this function calculates the area of circle
// process
float area = M_PI * radius ** 2;
return area;
}
static float calculateArea(int radius) {
// this function calculates the area of circle
// process
float area = Math.Pi * radius ** 2;
return area;
}
func calculateArea(radius int) {
// this function calculates the area of circle
// process
area := math.Pi * radius ** 2
return area
}
/**
* Calculates calculates the area of circle.
*
* @param args nothing passed in
*/
public static float calculateArea(int radius) {
// process
float area = Math.PI * Math.pow(radius, 2);
return area;
}
function calculateArea(radius) {
// this function calculates the area of circle
// process
const area = Math.PI * radius ** 2;
return area
}
def calculate_area(radius: int) -> float:
"""The calculate_area() function calculates the area of circle, returns float."""
# process
area = math.pi * radius ** 2
return area
Now that we know how to use a return statement, we should no longer print out results inside a function like in the last few chapters. It is much better style to retrun the value from a function and let the calling process decide what to do with it. Here is the example from last section, this time using return values:
1// Copyright (c) 2020 Mr. Coxall All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program calculates the area of circle
6
7#include <stdio.h>
8#include <math.h>
9
10float calculateArea(int radius) {
11 // this function calculates the area of circle
12
13 // process
14 float area = M_PI * radius ** 2;
15
16 return area;
17}
18
19int main() {
20 int radius;
21 float area = 0.0;
22
23 // input
24 printf("Enter the radius of a circle (cm): ");
25 scanf("%d", &radius);
26 printf("\n");
27
28 // call functions
29 area = calculateArea(radius);
30
31 // output
32 printf("The area is %f cm²\n", area);
33
34 printf("\nDone.\n");
35 return 0;
36}
1// Copyright (c) 2020 Mr. Coxall All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program calculates the area of circle
6
7#include <iostream>
8#include <cmath>
9
10
11float calculateArea(int radius) {
12 // this function calculates the area of circle
13
14 // process
15 float area = M_PI * radius ** 2;
16
17 return area;
18}
19
20int main() {
21 int radius = 0;
22 float area = 0.0;
23
24 // input
25 std::cout << "Enter the radius of a circle (cm): ";
26 std::cin >> radius;
27 std::cout << std::endl;
28
29 // call functions
30 area = calculateArea(radius);
31
32 // output
33 std::cout << "The area is " << area << " cm²\n";
34
35 std::cout << "\nDone." << std::endl;
36 return 0;
37}
1/* Created by: Mr. Coxall
2 * Created on: Sep 2020
3 * This program calculates the area of circle
4*/
5
6using System;
7
8/*
9 * The Program class
10 * Contains all methods for performing basic variable usage
11*/
12class Program {
13 static float calculateArea(int radius) {
14 // this function calculates the area of circle
15
16 // process
17 float area = Math.Pi * radius ** 2;
18
19 return area;
20 }
21
22 public static void Main (string[] args) {
23 int radius;
24 float area = 0.0;
25
26 // input
27 Console.Write("Enter the radius of a circle (cm): ");
28 radius = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
29 Console.WriteLine("");
30
31 // call functions
32 area = calculateArea(length, width);
33
34 // output
35 Console.WriteLine($"The area is {area} cm²");
36
37 Console.WriteLine("\nDone.");
38 }
39}
1/**
2 * Created by: Mr. Coxall
3 * Created on: Sep 2020
4 * This program calculates the area of circle
5 */
6
7 package main
8
9 import (
10 "fmt"
11 "math"
12 )
13
14 func calculateArea(radius int) {
15 // this function calculates the area of circle
16
17 // process
18 area := math.Pi * radius ** 2
19
20 return area
21 }
22
23 func main() {
24 var radius int
25 var area float
26
27 // input
28 fmt.Print("Enter the radius of a circle (cm): ")
29 fmt.Scanln(&radius)
30 fmt.Println()
31
32 // call functions
33 area = calculateArea(radius)
34
35 // output
36 fmt.Printf("The area is %d cm²\n", area)
37
38 fmt.Println("\nDone.")
39 }
40
1/*
2 * This program calculates the area of circle
3 *
4 * @author Mr Coxall
5 * @version 1.0
6 * @since 2020-09-01
7 */
8
9import java.util.Scanner;
10
11final class Main {
12 /**
13 * Calculates calculates the area of circle.
14 *
15 * @param args nothing passed in
16 */
17 public static float calculateArea(int radius) {
18 // process
19 float area = Math.PI * Math.pow(radius, 2);
20
21 return area;
22 }
23
24 private Main() {
25 // Prevent instantiation
26 // Optional: throw an exception e.g. AssertionError
27 // if this ever *is* called
28 throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot be instantiated");
29 }
30
31 /**
32 * Main entry point into program.
33 *
34 * @param args nothing passed in
35 */
36 public static float main(final String[] args) {
37 int radius;
38 float area = 0.0;
39
40 // input
41 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
42 System.out.print("Enter the radius of a circle (cm): ");
43 radius = scanner.nextInt();
44 System.out.println();
45
46 // call functions
47 area = calculateArea(radius);
48
49 // output
50 System.out.printf("The area is %d cm²%n", area);
51
52 System.out.println("\nDone.");
53 }
54}
1/**
2 * Created by: Mr. Coxall
3 * Created on: Sep 2020
4 * This program calculates the area of circle
5 */
6
7const prompt = require('prompt-sync')();
8
9function calculateArea(radius) {
10 // this function calculates the area of circle
11
12 // process
13 const area = Math.PI * radius ** 2;
14
15 return area
16}
17
18// input
19const radius = parseInt(prompt("Enter the radius of a circle (cm): "));
20console.log();
21
22// call functions
23area = calculateArea(radius);
24
25// output
26console.log(`The area is ${area} cm²`);
27
28console.log("\nDone.");
1#!/usr/bin/env python3
2"""
3Created by: Mr. Coxall
4Created on: Sep 2020
5This module calculates the area of circle
6"""
7
8import math
9
10
11def calculate_area(radius: int) -> float:
12 """The calculate_area() function calculates the area of circle, returns float."""
13
14 # process
15 area = math.pi * radius ** 2
16
17 return area
18
19
20def main() -> None:
21 """The main() function just calls other functions, returns None."""
22
23 # input
24 radius = int(input("Enter the radius of a circle (cm): "))
25 print("")
26
27 # call functions
28 area = calculate_area(radius)
29
30 # output
31 print(f"The area is {area:.2f} cm²")
32
33 print("\nDone.")
34
35
36if __name__ == "__main__":
37 main()
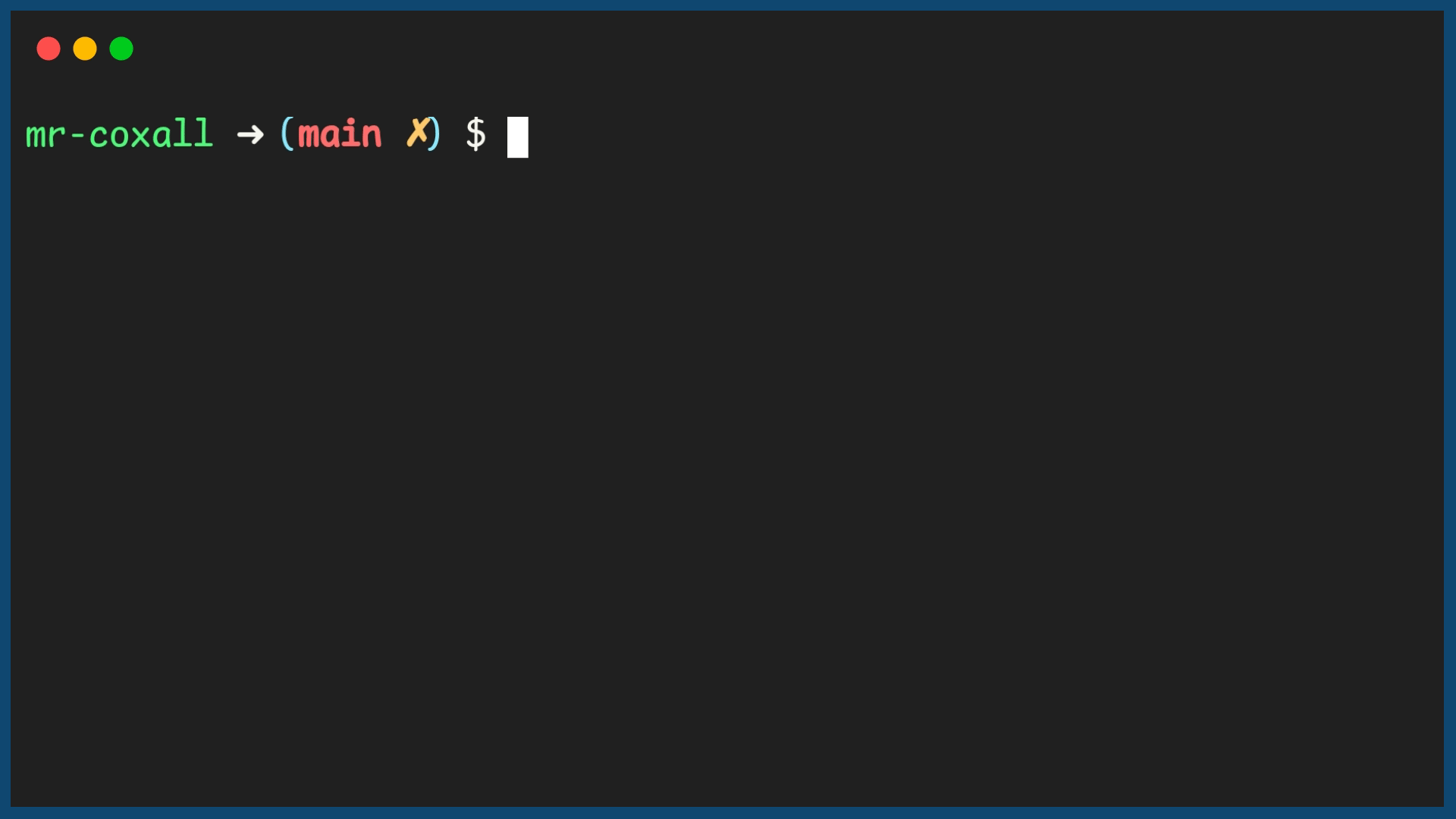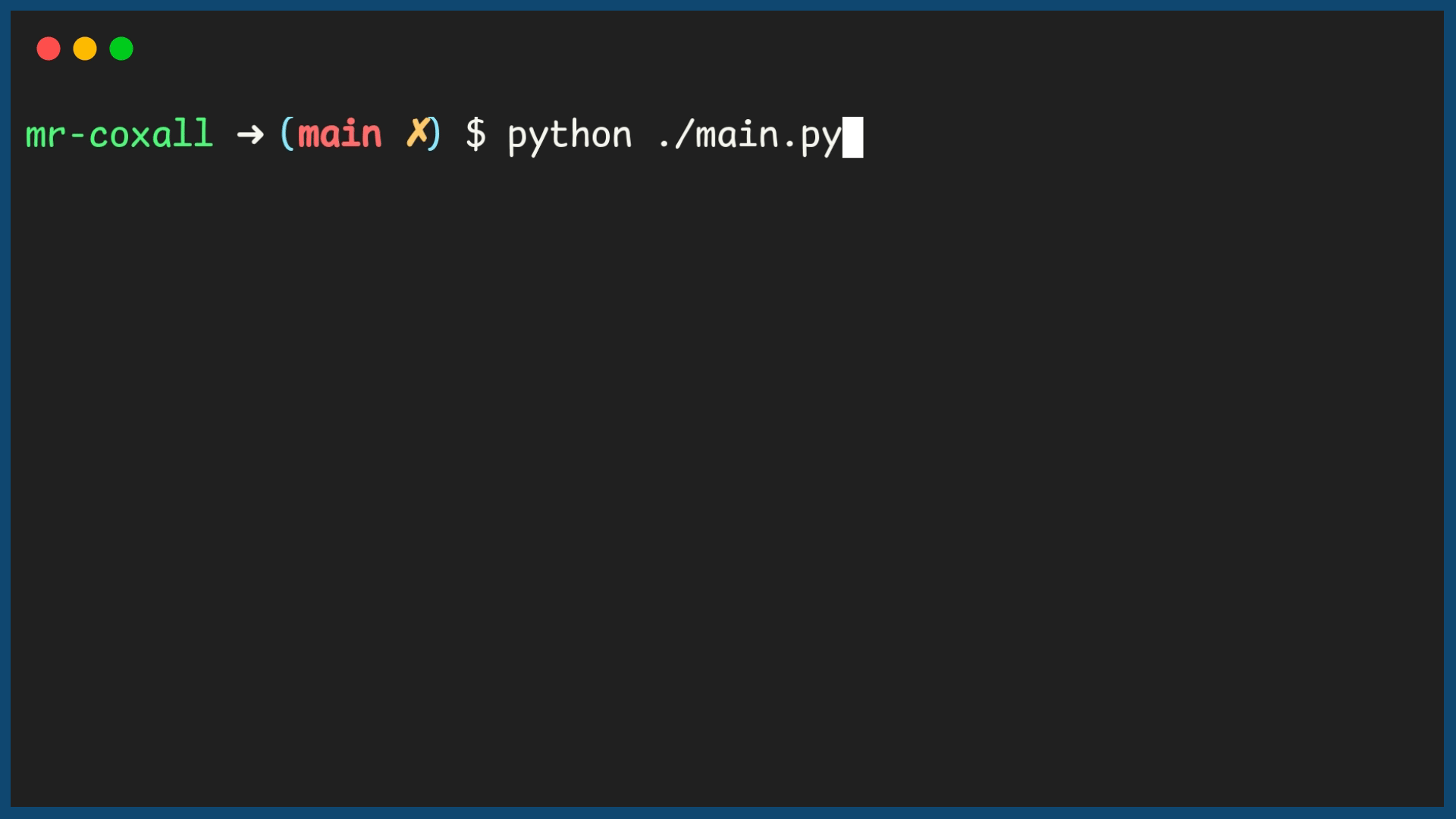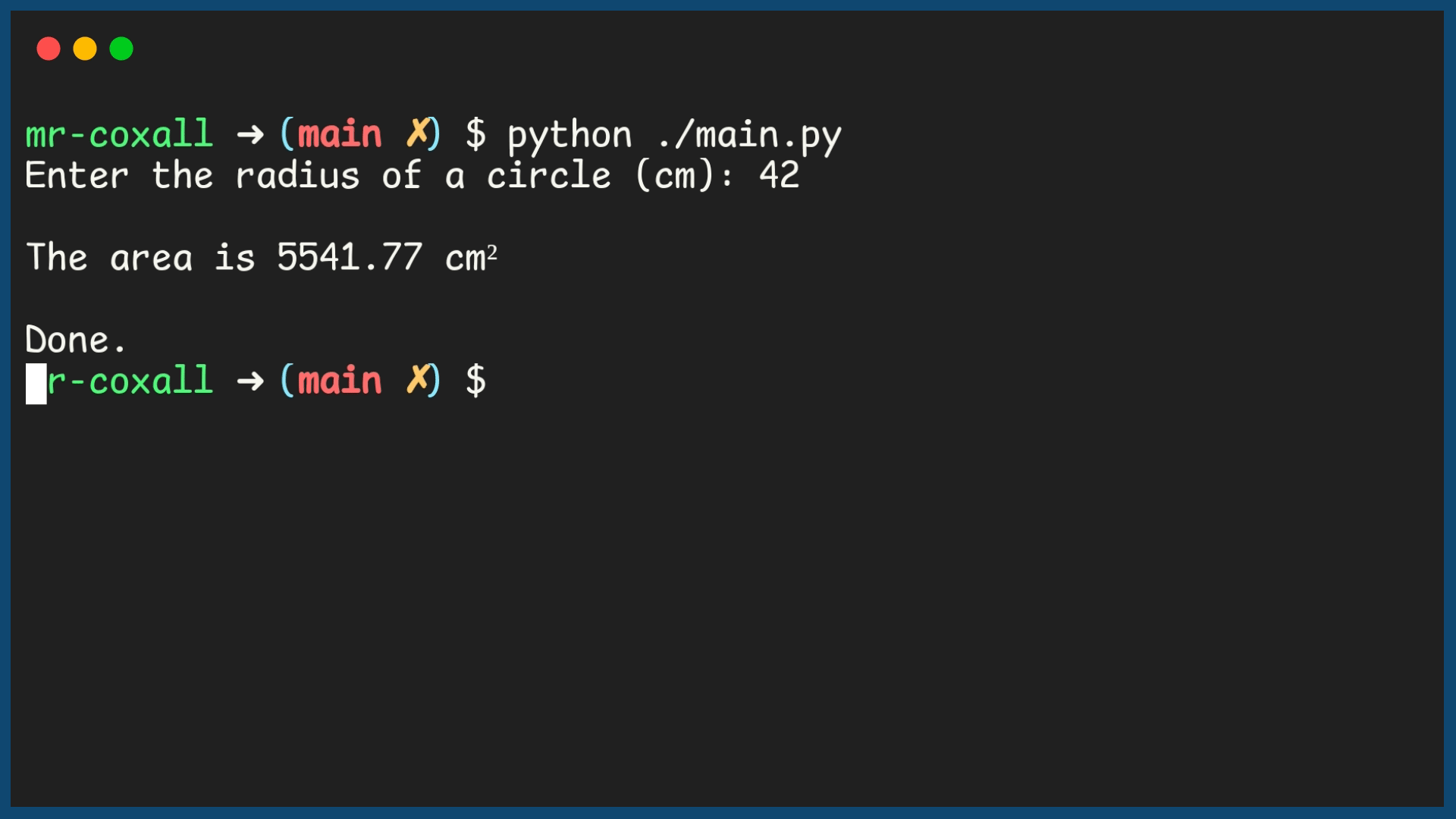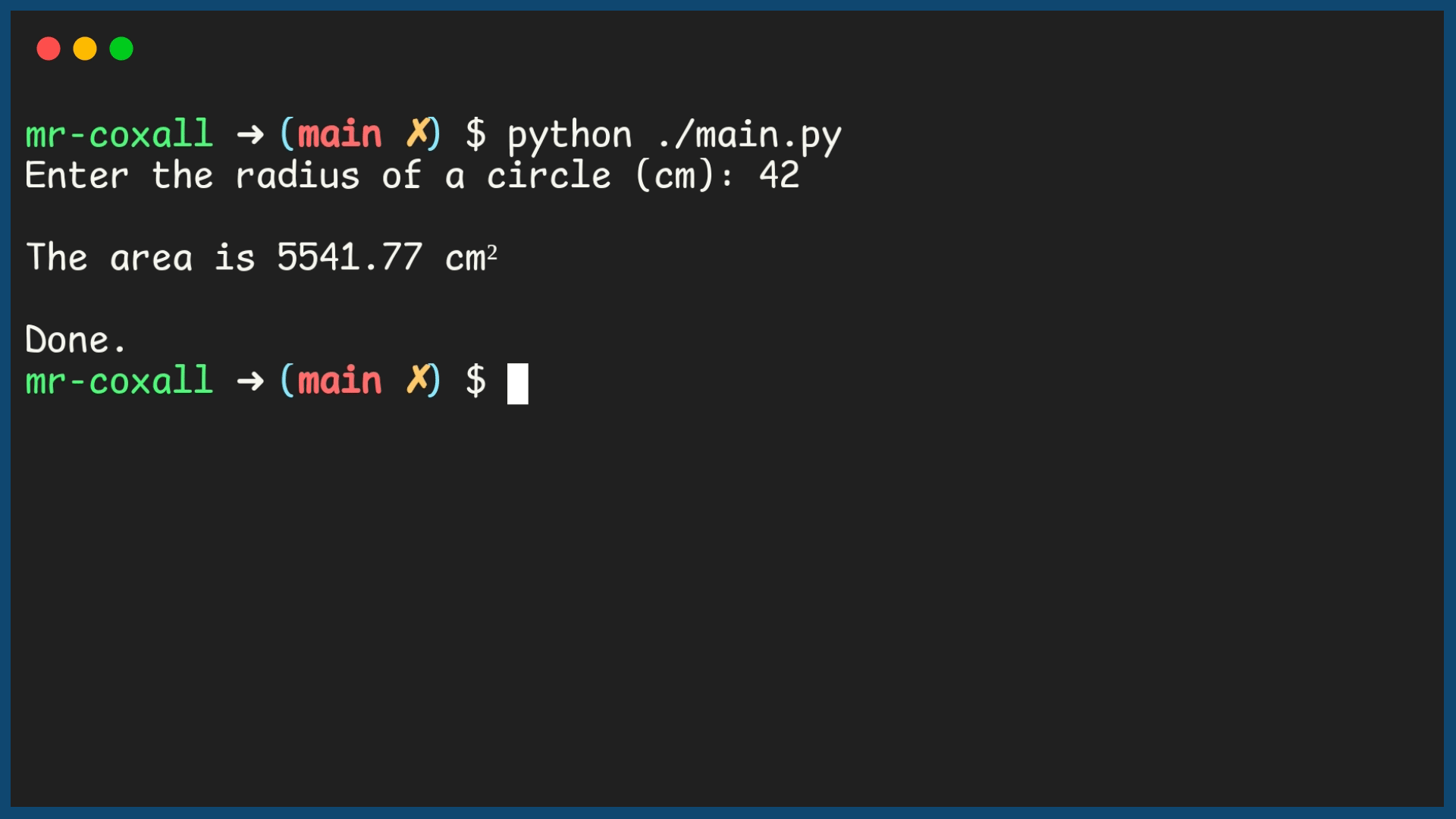
Example Output