By Value or By Reference
The second method of transferring information to a function is to pass it By Reference. This means that a pointer or reference to where the data is stored in memory is passed to the function and not a copy of the data. Since a pointer to where the data exists has been passed, if you actually change the value of the data in the function, the actual values of the data in the main program where the function was called from will also be changed. This can be very powerful but also very dangerous. Be careful passing parameters By Reference, you might mistakenly change a value when that is not what you or someone else is expecting. The rule of thumb is that unless there is a really good reason to pass something By Reference, you never do and you always pass parameters By Value (even though it takes up more space in memory).
Each language has its own syntax on how to declare you are going to accept a value by reference when you are declaring a function here is an example:
Code for Function passing a value By Reference
1// Copyright (c) 2020 Mr. Coxall All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program uses a function by reference
6
7#include <stdio.h>
8
9void addOne(int *someNumber) {
10 // this function adds one by reference
11 (*someNumber)++;
12}
13
14int main() {
15 // this function uses a function by reference
16 int someNumber;
17
18 // input
19 printf("Enter a number: ");
20 scanf("%d", &someNumber);
21
22 // process
23 addOne(&someNumber);
24
25 // output
26 printf("The number plus one is: %d \n", someNumber);
27
28 printf("\nDone.\n");
29 return 0;
30}
1// Copyright (c) 2020 Mr. Coxall All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program uses a function by reference
6
7#include <iostream>
8
9void addOne(int &someNumber) {
10 // this function adds one, by reference
11 someNumber = someNumber + 1;
12}
13
14int main() {
15 // this function uses a function by reference
16 int someNumber;
17
18 // input
19 std::cout << "Enter a number: ";
20 std::cin >> someNumber;
21
22 // process
23 addOne(someNumber);
24
25 // output
26 std::cout << "The number plus one is: " << someNumber << std::endl;
27
28 std::cout << "\nDone." << std::endl;
29}
1/* Created by: Mr. Coxall
2 * Created on: Sep 2020
3 * This program uses a function by reference
4*/
5
6using System;
7
8/*
9 * The Program class
10*/
11class Program {
12 static void AddOne(ref int someNumber) {
13 // this function adds one to the parameter, by reference
14 someNumber = someNumber + 1;
15 }
16
17 static void Main() {
18 // this function uses a function by reference
19 int someNumber;
20
21 // input
22 Console.Write("Enter a number: ");
23 someNumber = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
24
25 // process
26 AddOne(ref someNumber);
27
28 // output
29 Console.WriteLine("The number plus one is: {0}", someNumber);
30
31 Console.WriteLine("\nDone.");
32 }
33}
1/**
2 * Created by: Mr. Coxall
3 * Created on: Sep 2020
4 * This program uses a function by reference
5 */
6
7package main
8
9import "fmt"
10
11func addOne(someVariable *int) {
12 // this function adds one to the variable passed in, by reference
13 *someVariable = *someVariable + 1
14}
15
16func main() {
17 // this function uses a function by reference
18 var someNumber int
19
20 // input
21 fmt.Print("Enter a number: ")
22 fmt.Scan(&someNumber)
23
24 // Process
25 addOne(&someNumber)
26
27 // Output
28 fmt.Println("The number plus one is:", someNumber)
29
30 fmt.Println("\nDone.")
31}
1/*
2 * This program uses a function by reference
3 *
4 * @author Mr Coxall
5 * @version 1.0
6 * @since 2020-09-01
7 */
8
9import java.util.Scanner;
10
11public class Main {
12
13 /**
14 * This function adds one to a number, by reference.
15 * @param someNumber
16 */
17 public static void addOne(int[] someNumber) {
18 someNumber[0] = someNumber[0] + 1;
19 }
20
21 public static void main(String[] args) {
22 // this function uses a function by reference
23
24 // In Java, you can pass a variable by reference by using an array
25 int[] someVariable = new int[1];
26
27 // input
28 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
29 System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
30 someVariable[0] = input.nextInt();
31
32 // process
33 addOne(someVariable);
34
35 // output
36 System.out.println("The number plus one is: " + someVariable[0]);
37
38 System.out.println("\nDone.");
39 }
40}
1/*
2Created by: Mr. Coxall
3Created on: Sep 2020
4This module uses a function by reference
5*/
6
7function addOne(someVariable) {
8 // The addOne() function adds 1, by reference
9 someVariable[0] = someVariable[0] + 1;
10}
11
12const prompt = require('prompt-sync')()
13// In JavaScript, you can pass a variable by reference by using an array
14const someNumber = [];
15
16// Input
17const tempVar = parseInt(prompt("Enter a number: "));
18someNumber.push(tempVar);
19
20// Process
21addOne(someNumber);
22
23// Output
24console.log(`The number plus one is: ` + someNumber[0]);
25
26console.log("\nDone.");
1#!/usr/bin/env python3
2"""
3Created by: Mr. Coxall
4Created on: Sep 2020
5This module uses a function by reference
6"""
7
8
9def add_one(someVariable: List[int]) -> None:
10 """The add_one() function adds 1, by reference, returns str."""
11 # in python the only way to pass by reference is to pass the whole list
12
13 someVariable[0] = someVariable[0] + 1
14
15
16def main() -> None:
17 """The main() this function gets a number and calls the add_one function, returns None."""
18 someNumber = []
19
20 # input
21 temp_var = int(input("Enter a number: "))
22 someNumber.append(temp_var)
23
24 # process
25 add_one(someNumber)
26
27 # output
28 print(f"The number plus one is: {someNumber[0]}")
29
30 print("\nDone.")
31
32
33if __name__ == "__main__":
34 main()
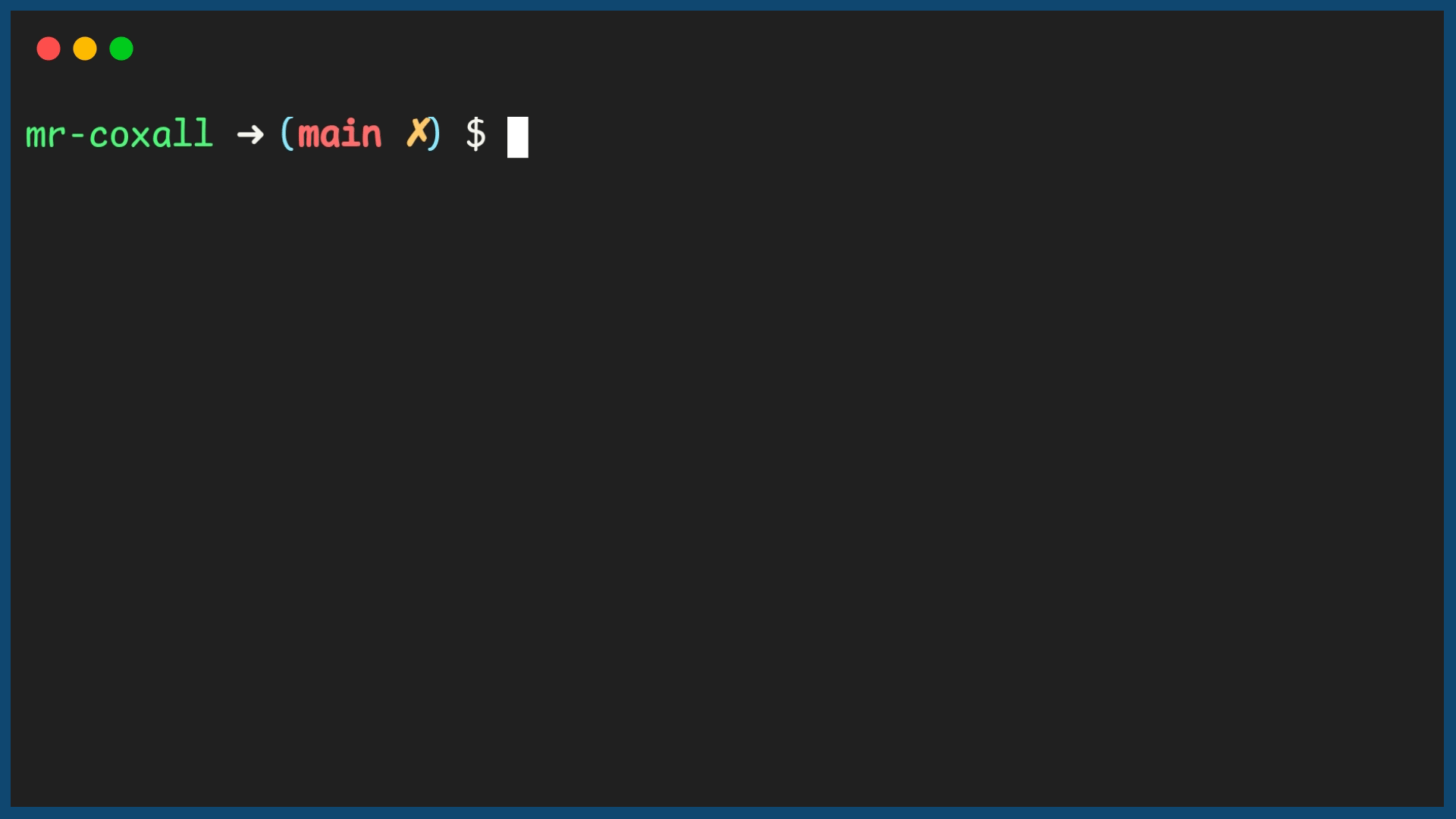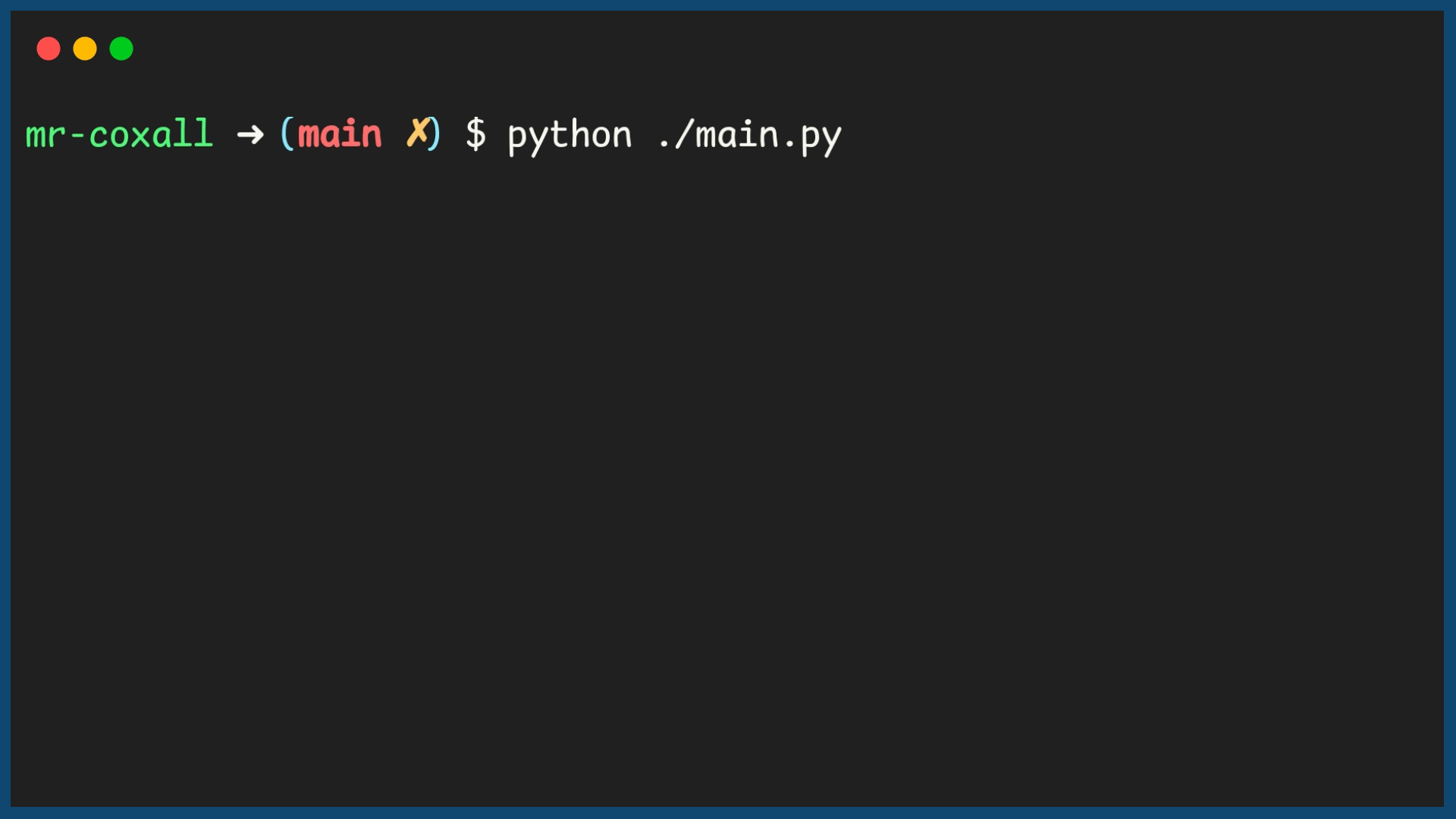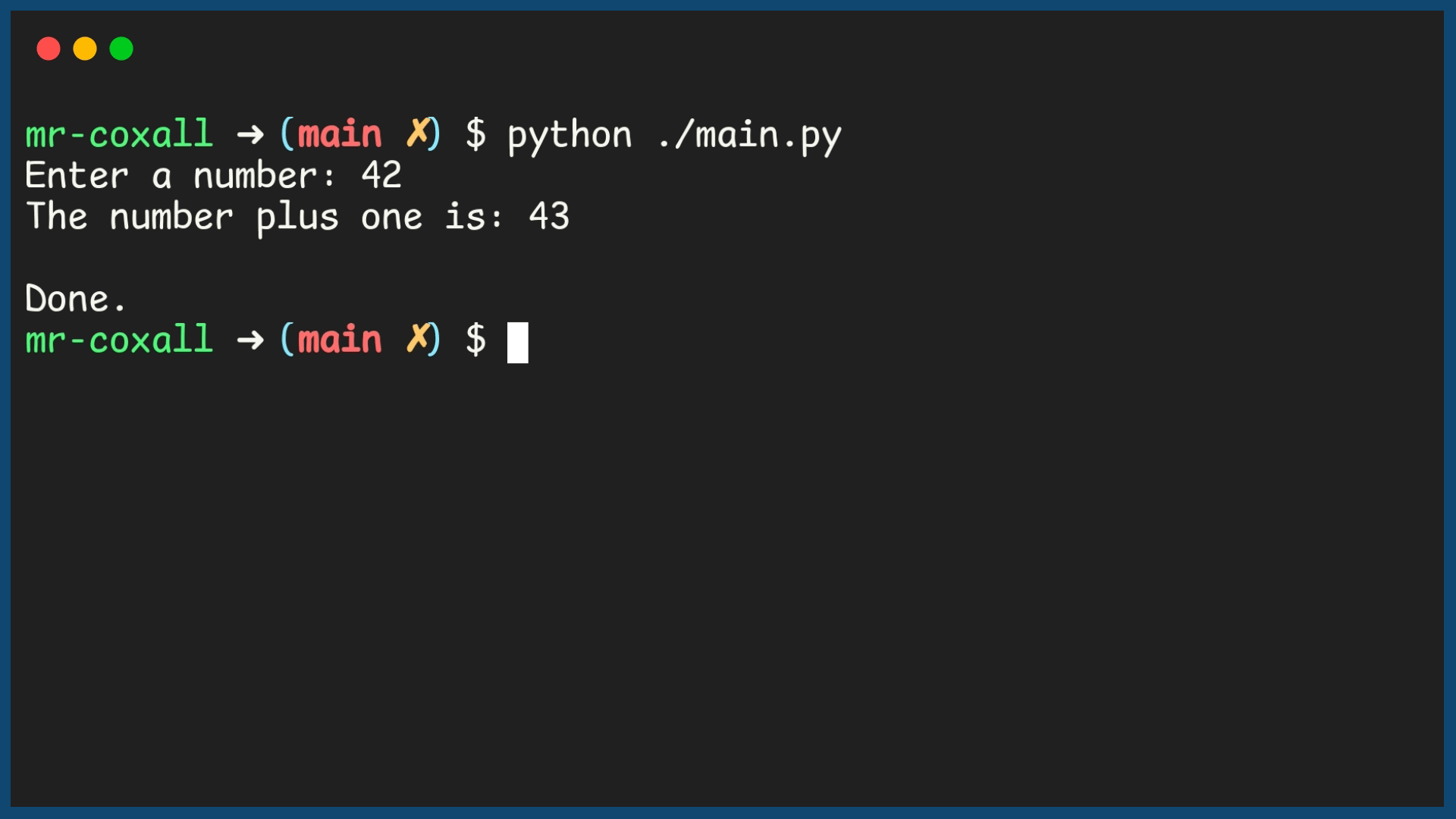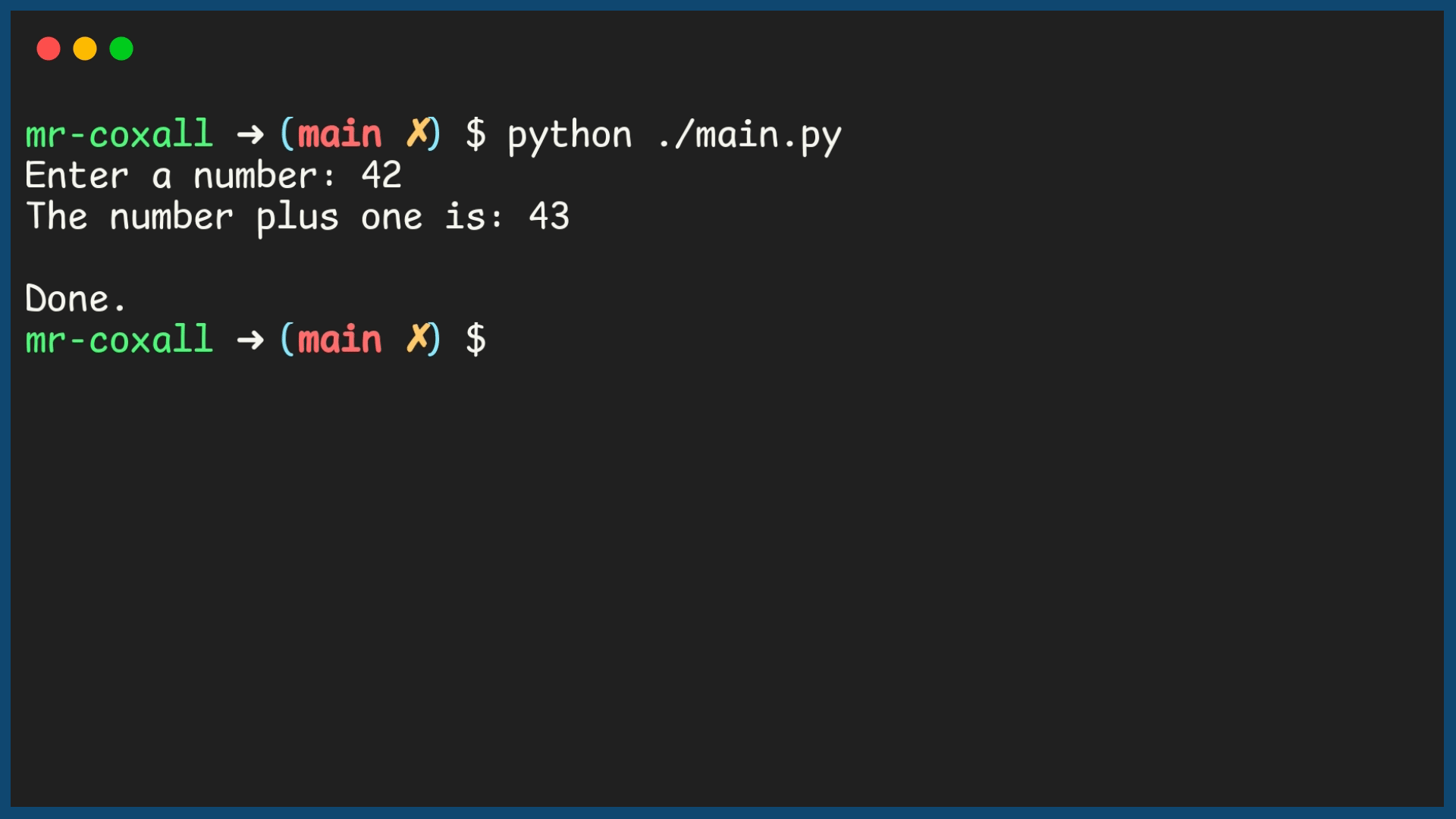
Example Output