Nested Loops
The placing of one loop inside the body of another loop is called nesting. When you, “nest” two loops, the outer loop takes control of the number of complete repetitions of the inner loop. How this works is that the first pass of the outer loop triggers the inner loop, which executes to completion. Then the second pass of the outer loop triggers the inner loop again. This repeats until the outer loop finishes.
A Nested for loop (in most computer programming languages), takes the generic form of:
FOR counter1 in range(n)
FOR counter2 in range(m)
statement(s)
…
END
END
or using While loops:
WHILE counter1 <= n :
WHILE counter2 <= m :
statement(s)
…
counter2 = counter2 + 1
END
counter2 = 0
…
counter1 = counter1 + 1
END
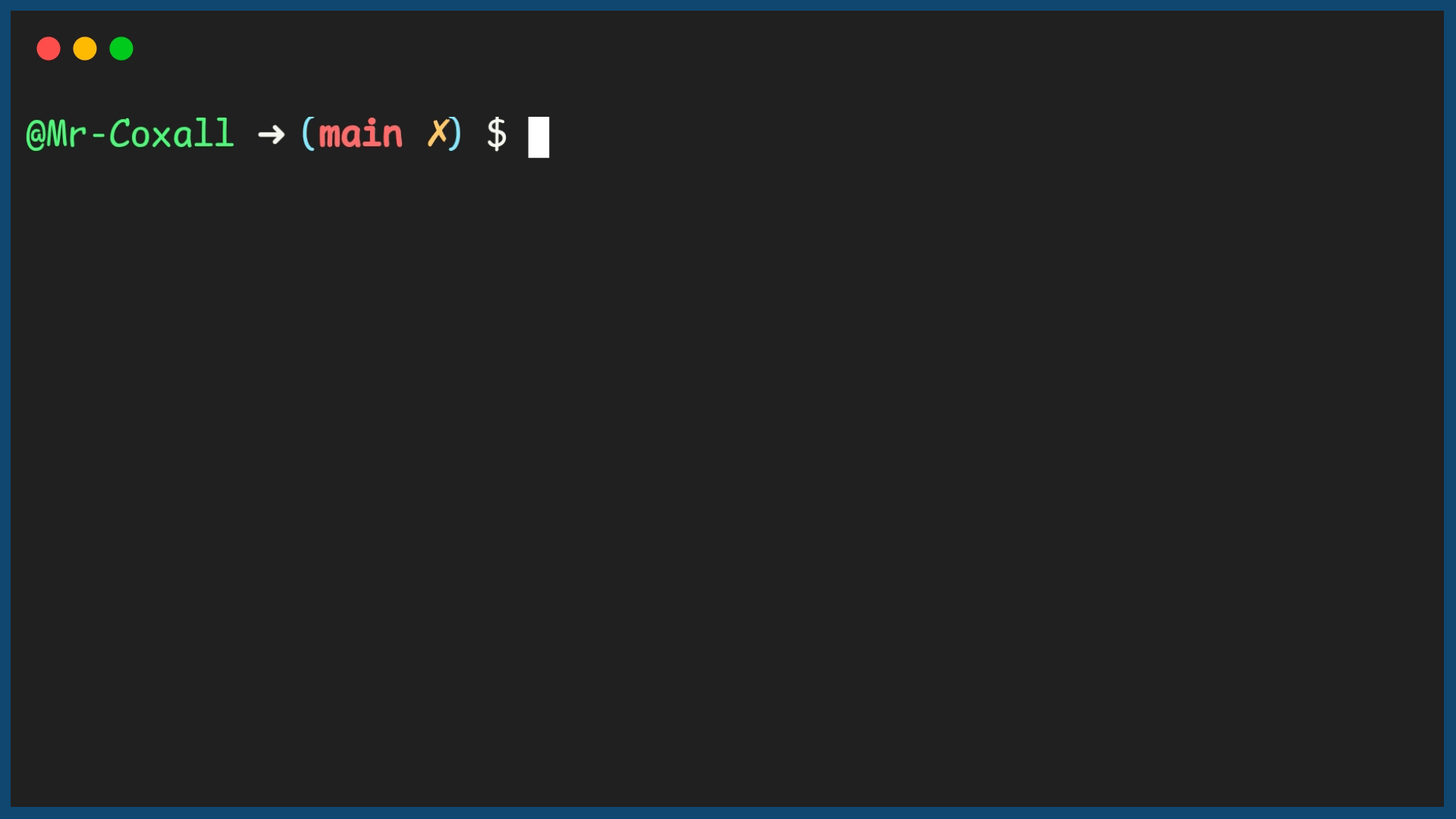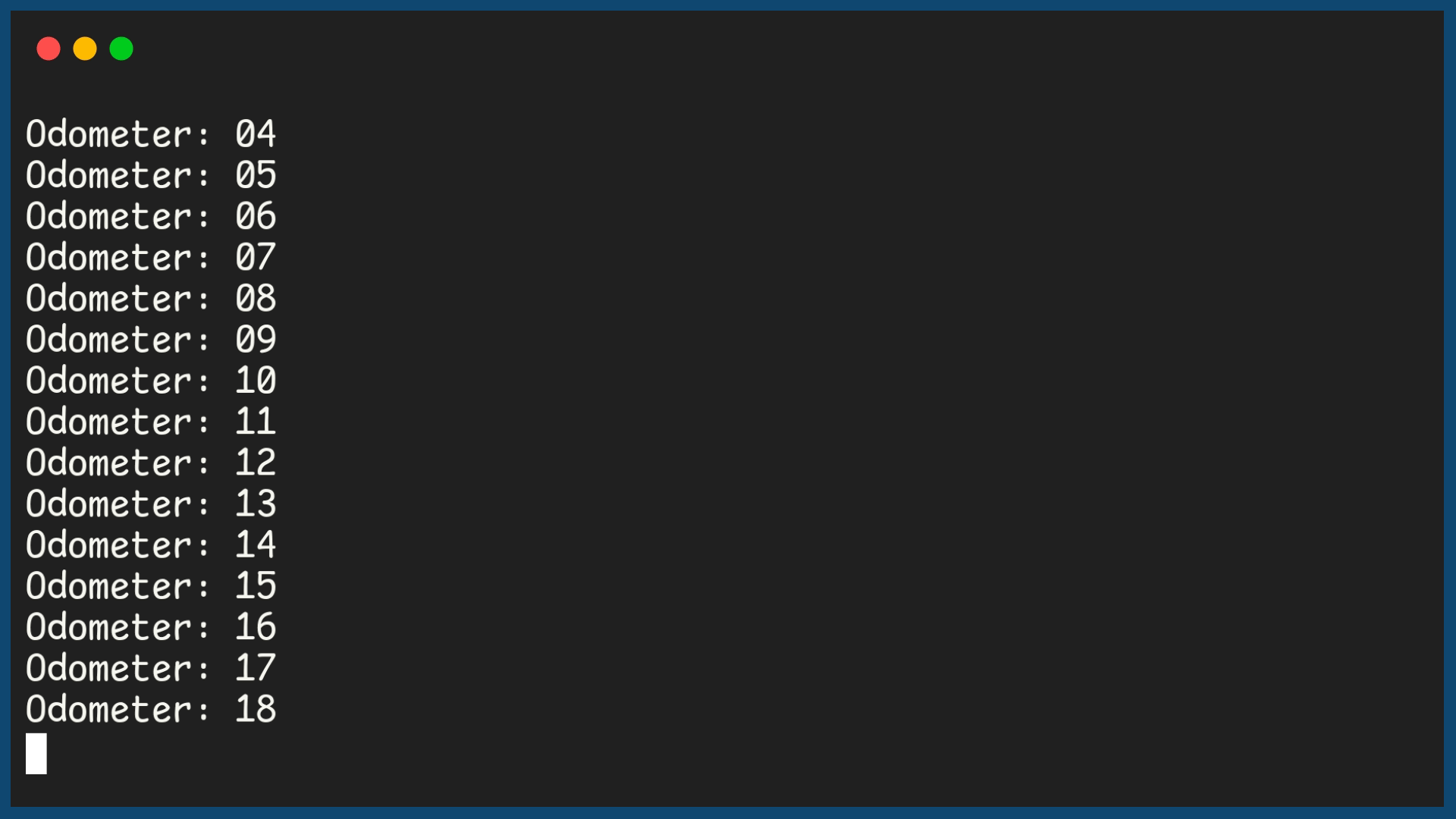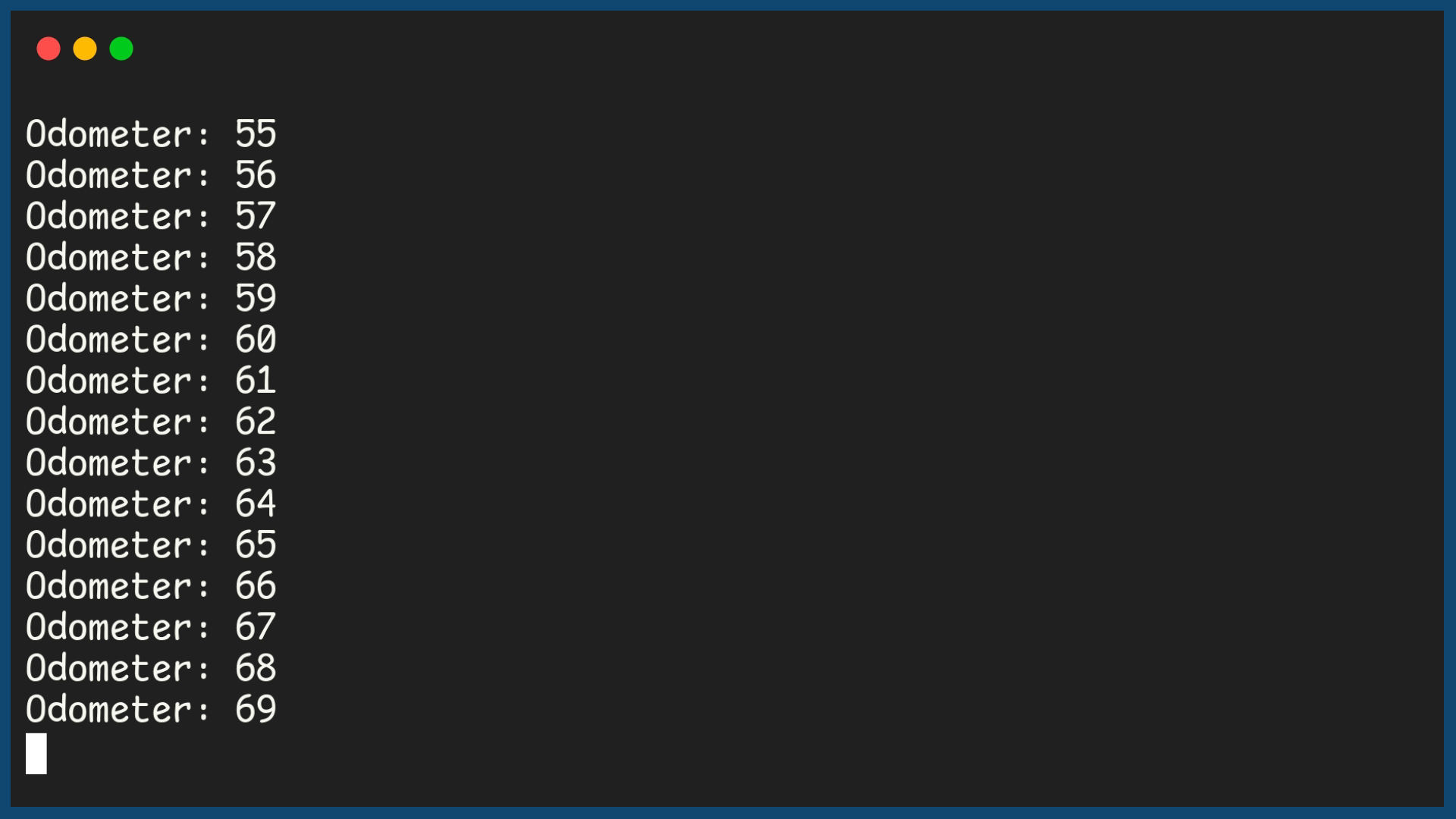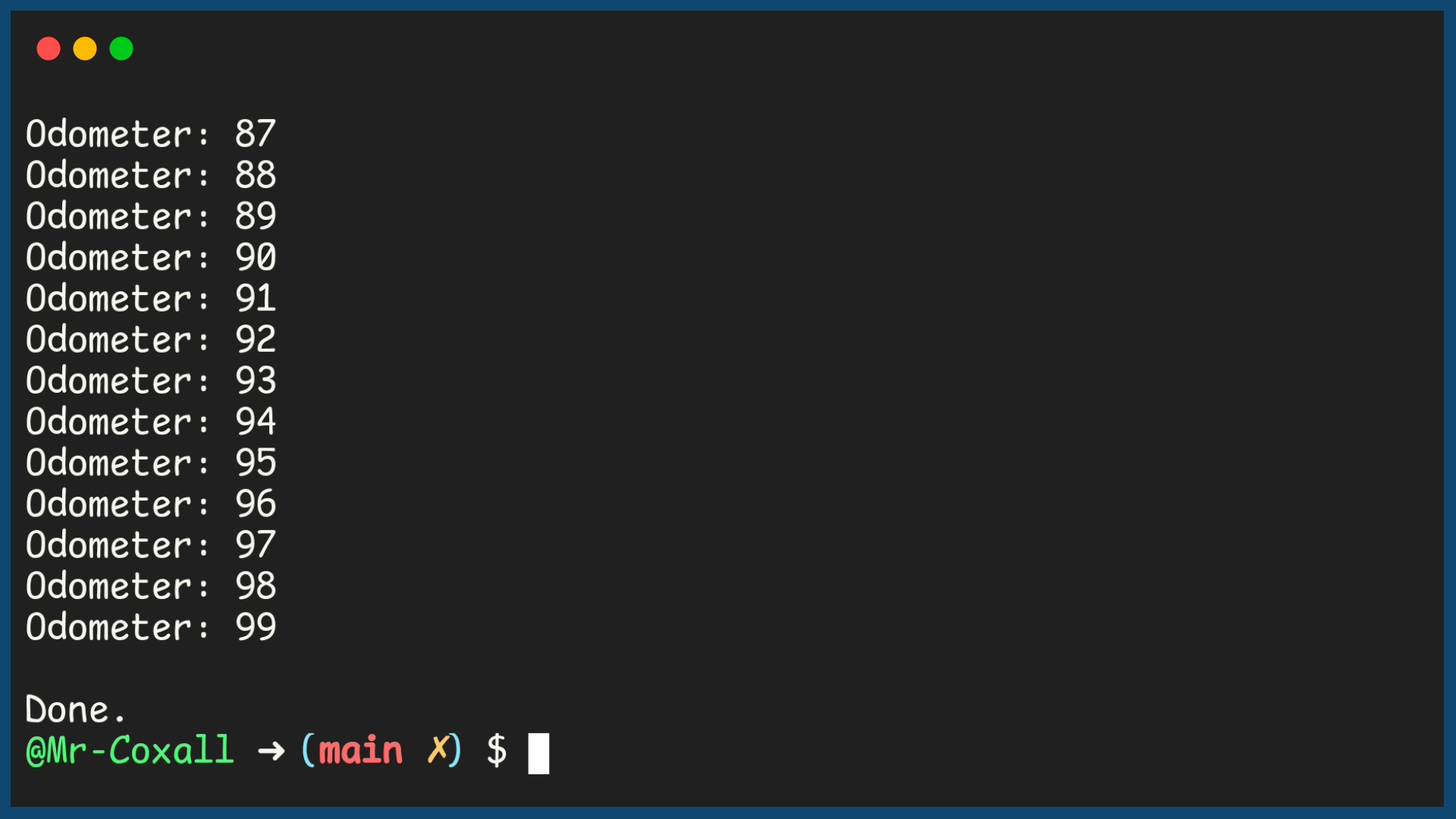
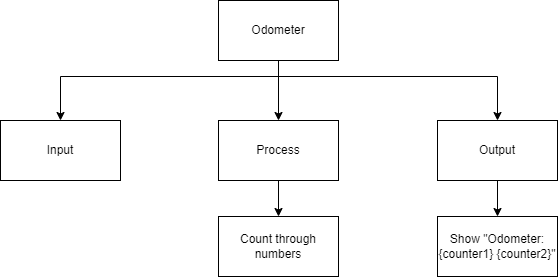
In this example program, the output shows a 2 digit odometer, using a Nested loop.
Top-Down Design for Nested loops
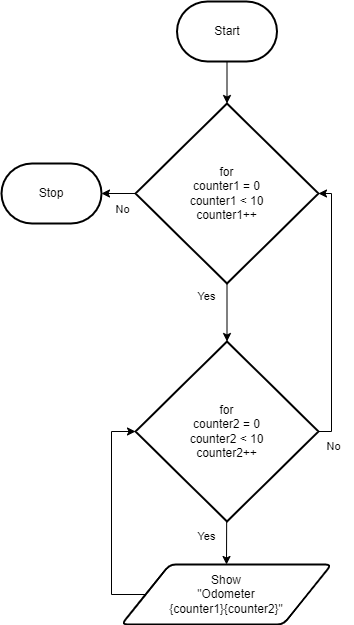
Flowchart for Nested loops
Pseudocode for Nested loops
FOR counter1 in range(10)
FOR counter2 in range(10)
SHOW Odometer {counter1}{counter2}
END
END
Code for the Nested loops
1// Copyright (c) 2020 Mr. Coxall All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program uses a nested loop
6
7#include <stdio.h>
8
9int main() {
10 // this function uses a nested loop
11
12 // process & output
13 for (int counter1 = 0; counter1 < 10; counter1++) {
14 for (int counter2 = 0; counter2 < 10; counter2++) {
15 printf("Odometer: %d%d\n", counter1, counter2);
16 }
17 }
18
19 printf("\nDone.\n");
20 return 0;
21}
1// Copyright (c) 2020 St. Mother Teresa HS All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program uses a nested loop
6
7#include <iostream>
8
9int main() {
10 // this function uses a nested loop
11
12 // process & output
13 for (int counter1 = 0; counter1 < 10; counter1++) {
14 for (int counter2 = 0; counter2 < 10; counter2++) {
15 std::cout << "Odometer: " << counter1 << counter2 << std::endl;
16 }
17 }
18
19 std::cout << "\nDone." << std::endl;
20 return 0;
21}
1/* Created by: Mr. Coxall
2 * Created on: Sep 2020
3 * This program uses a nested loop
4*/
5
6using System;
7
8/*
9 * The Program class
10*/
11class Program {
12 static void Main() {
13 // this function uses a nested loop
14
15 // process & output
16 for (int counter1 = 0; counter1 < 10; counter1++) {
17 for (int counter2 = 0; counter2 < 10; counter2++) {
18 Console.WriteLine("Odometer: " + counter1 + counter2);
19 }
20 }
21
22 Console.WriteLine("\nDone.");
23 }
24}
1/**
2 * Created by: Mr. Coxall
3 * Created on: Sep 2020
4 * This program uses a nested loop
5 */
6
7package main
8
9import (
10 "fmt"
11)
12
13func main() {
14 // this function uses a nested loop
15
16 var counter1 int
17 var counter2 int
18
19 // process & output
20 for counter1 < 10 {
21 for counter2 < 10 {
22 fmt.Printf("Odometer:%d%d\n", counter1, counter2)
23 counter2++
24 }
25 counter2 = 0
26 counter1++
27 }
28
29 fmt.Println("\nDone.")
30}
1/*
2 * This program uses a nested loop
3 *
4 * @author Mr Coxall
5 * @version 1.0
6 * @since 2020-09-01
7 */
8
9public class Main {
10 public static void main(String[] args) {
11 // this function uses a nested loop
12
13 // process & output
14 for (int counter1 = 0; counter1 < 10; counter1++) {
15 for (int counter2 = 0; counter2 < 10; counter2++) {
16 System.out.println("Odometer: %d%d".formatted(counter1, counter2));
17 }
18 }
19
20 System.out.println("\nDone.");
21 }
22}
1/* Created by: Mr. Coxall
2 * Created on: Sep 2020
3 * This program uses a nested loop
4 */
5
6// process & output
7for (var counter1 = 0; counter1 < 10; counter1++) {
8 for (var counter2 = 0; counter2 < 10; counter2++) {
9 console.log(`Odometer: ${counter1}${counter2}`)
10 }
11}
12
13console.log("\nDone.")
1#!/usr/bin/env python3
2"""
3Created by: Mr. Coxall
4Created on: Sep 2020
5This module uses a nested loop
6"""
7import time
8
9
10def main() -> None:
11 """The main() function uses a nested loop, returns None."""
12
13 # process & output
14 for counter1 in range(10):
15 for counter2 in range(10):
16 print(f"Odometer: {counter1}{counter2}")
17 time.sleep(0.25)
18
19 print("\nDone.")
20
21
22if __name__ == "__main__":
23 main()
Example Output