Compound Boolean Expressions
Just before we looked at the If … Then statement we looked at Boolean expressions. Boolean expressions have two and only two potential answers, either they are true or false. So far we have looked at just simple Boolean expression, with just one comparison. A Boolean expression can actually have more than one comparison and be quite complex. A compound Boolean expression is generated by combining more than one simple Boolean expression together with a logical operator NOT, AND & OR. NOT is used to form an expression that evaluates to True only when the operand is false. AND is used to form an expression that evaluates to True only when both operands are true. OR is used to form an expression that evaluates to true when either operand is true.
Here is a truth table for each operator:
NOT Truth Table
A |
NOT A |
|---|---|
True |
False |
False |
True |
AND Truth Table
A |
B |
A AND B |
|---|---|---|
True |
True |
True |
True |
False |
False |
False |
True |
False |
False |
False |
False |
OR Truth Table
A |
B |
A OR B |
|---|---|---|
True |
True |
True |
True |
False |
True |
False |
True |
True |
False |
False |
False |
The general form in a programming language for a compound Boolean expression is:
NOT
AND
OR
In some programming languages the operators are simply the words not, and & or. In others they are “!” for NOT, “&&” for AND & “||” for OR.
In this example program, the user is asked to enter a term mark and a final project mark. The program then tells the user if they passed the course or not. The rule for passing the course is that the student must have a term mark of at least 50% and a final project mark of at least 50. The program uses a compound Boolean expression to determine if the student passed the course.
Top-Down Design for Compound Boolean Expression statement
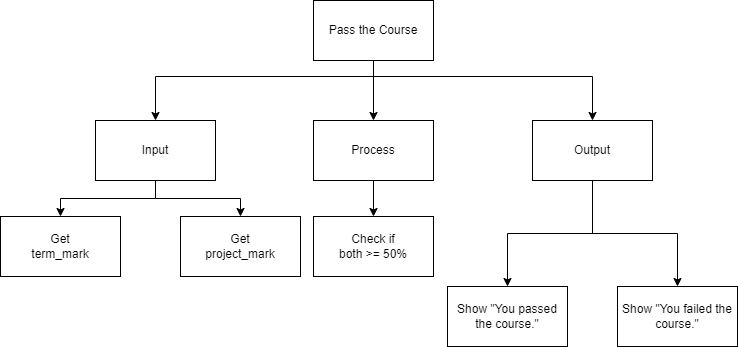
Flowchart for Compound Boolean Expression statement
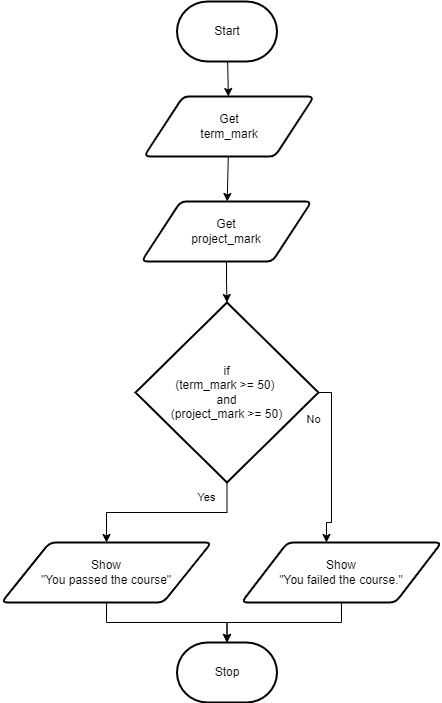
Pseudocode for Compound Boolean Expression statement
Code for Compound Boolean Expression statement
1// Copyright (c) 2020 Mr. Coxall All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program uses a compound boolean statement
6
7#include <stdio.h>
8
9int main() {
10 // this function uses a compound boolean statement
11 int termMark;
12 int projectMark;
13
14 // input
15 printf("Enter term mark (as %%): ");
16 scanf("%d", &termMark);
17 printf("Enter project mark (as %%): ");
18 scanf("%d", &projectMark);
19 printf("\n");
20
21 // process & output
22 if (termMark >= 50 && projectMark >= 50) {
23 printf("You passed the course.\n");
24 } else {
25 printf("You did not pass the course.\n");
26 }
27
28 printf("\nDone.\n");
29 return 0;
30}
1// Copyright (c) 2020 St. Mother Teresa HS All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program uses a compound boolean statement
6
7#include <iostream>
8
9int main() {
10 // this function uses a compound boolean statement
11 int termMark;
12 int projectMark;
13
14 // input
15 std::cout << "Enter term mark (as %): ";
16 std::cin >> termMark;
17 std::cout << "Enter project mark (as %): ";
18 std::cin >> projectMark;
19 std::cout << std::endl;
20
21 // process & output
22 if (termMark >= 50 && projectMark >= 50) {
23 std::cout << "You passed the course." << std::endl;
24 } else {
25 std::cout << "You did not pass the course." << std::endl;
26 }
27
28 std::cout << "\nDone." << std::endl;
29 return 0;
30}
1/* Created by: Mr. Coxall
2 * Created on: Sep 2020
3 * This program uses a compound boolean statement
4*/
5
6using System;
7
8/*
9 * The Program class
10*/
11class Program {
12 static void Main() {
13 // this function uses a compound boolean statement
14
15 // input
16 Console.Write("Enter term mark (as %): ");
17 int termMark = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
18 Console.Write("Enter project mark (as %): ");
19 int projectMark = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
20 Console.WriteLine();
21
22 // process & output
23 if (termMark >= 50 && projectMark >= 50) {
24 Console.WriteLine("You passed the course.");
25 } else {
26 Console.WriteLine("You did not pass the course.");
27 }
28
29 Console.WriteLine("\nDone.");
30 }
31}
1/**
2 * Created by: Mr. Coxall
3 * Created on: Sep 2020
4 * This program uses a compound boolean statement
5 */
6
7package main
8
9import (
10 "fmt"
11)
12
13func main() {
14 // this function uses a compound boolean statement
15
16 // input
17 var termMark int
18 var projectMark int
19
20 fmt.Print("Enter term mark (as %): ")
21 fmt.Scanln(&termMark)
22 fmt.Print("Enter project mark (as %): ")
23 fmt.Scanln(&projectMark)
24 fmt.Println()
25
26 // process & output
27 if termMark >= 50 && projectMark >= 50 {
28 fmt.Println("You passed the course.")
29 } else {
30 fmt.Println("You did not pass the course.")
31 }
32
33 fmt.Println("\nDone.")
34}
1/*
2 * This program uses a compound boolean statement
3 *
4 * @author Mr Coxall
5 * @version 1.0
6 * @since 2020-09-01
7 */
8
9import java.util.Scanner;
10
11public class Main {
12 public static void main(String[] args) {
13 // this function uses a compound boolean statement
14
15 // create Scanner object for user input
16 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
17
18 // input
19 System.out.print("Enter term mark (as %): ");
20 int termMark = scanner.nextInt();
21 System.out.print("Enter project mark (as %): ");
22 int projectMark = scanner.nextInt();
23 System.out.println();
24
25 // process & output
26 if (termMark >= 50 && projectMark >= 50) {
27 System.out.println("You passed the course.");
28 } else {
29 System.out.println("You did not pass the course.");
30 }
31
32 // close the Scanner object
33 scanner.close();
34 System.out.println("\nDone.");
35 }
36}
1/* Created by: Mr. Coxall
2 * Created on: Sep 2020
3 * This program uses a compound boolean statement
4 */
5
6const prompt = require("prompt-sync")()
7
8// input
9const termMark = parseInt(prompt("Enter term mark (as %): "))
10const projectMark = parseInt(prompt("Enter project mark (as %): "))
11console.log("");
12
13// process & output
14if (termMark >= 50 && projectMark >= 50) {
15 console.log("You passed the course.")
16} else {
17 console.log("You did not pass the course.")
18}
19
20console.log("\nDone.")
1#!/usr/bin/env python3
2"""
3Created by: Mr. Coxall
4Created on: Sep 2020
5This module uses a compound boolean statement
6"""
7
8
9def main() -> None:
10 """The main() function uses a compound boolean statement, returns None."""
11
12 # input
13 term_mark = int(input("Enter term mark (as %): "))
14 project_mark = int(input("Enter project mark (as %): "))
15 print("")
16
17 # process & output
18 if term_mark >= 50 and project_mark >= 50:
19 print("You passed the course.")
20 else:
21 print("You did not pass the course.")
22
23 print("\nDone.")
24
25
26if __name__ == "__main__":
27 main()
Example Output