Lists
Since in many programming languages, when you create an array the size must be set during coding so that the memory can be allocated when it is compiled, there is no way to dynamically change the size of an array during run time. This can be a huge disadvantage. One great example of wanting to have dynamic arrays is the classic video game, Space Invaders. If you imagine that all the lazer you shoot are held in an array, then how big should the array be? You have no idea how fast the user can press the “A” button. You can not tell how many lazers might be on the screen at any given time! If you cannot change the size of the array, what can we do, just making a “huge” array is wasteful and not really practical. Fortunately in many programming languages there is a data structure called a list.
A List is similar to an array in that it is an ordered grouping of data. You still reference the items in the list using a positive integer index. The key difference is that the size of the list can shrink and grow, during run time as needed. As you need to add items, you just use an “Add” (or something similar like append). To remove an item you use “Remove” (or something similar like pop). The list usually has many useful methods for adding, sorting, clearing, finding the length an so on.
Here is an example of creating a list of items:
Code for Creating a List
// No list or Linked List standard in C.
// You can create dynamic arrays by using maloc(), but that is beyond the scope of this book.
// https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/dynamic-array-in-c/
1// Copyright (c) 2020 St. Mother Teresa HS All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program program uses a list
6
7#include <iostream>
8#include <list> // need this for Lists
9
10int main() {
11 // this function uses a list
12 std::list<std::string> words;
13 std::string tempWord = "Go";
14 std::list<std::string> reversedWords;
15
16 // input
17 std::cout << "Please enter 1 word at a time. Enter 'S' to end." << std::endl;
18
19 while (tempWord != "STOP") {
20 std::cout << "Enter a word: ";
21 std::cin >> tempWord;
22 words.push_back(tempWord);
23 }
24
25 words.pop_back(); // remove the "Stop" that was added
26 std::cout << "" << std::endl;
27
28 // reversed words
29 std::cout << "Here are the words reversed.:" << std::endl;
30 while (!words.empty()) {
31 std::cout << words.back() << std::endl;
32 words.pop_back();
33 }
34
35 std::cout << "\nDone." << std::endl;
36}
1/* Created by: Mr. Coxall
2 * Created on: Sep 2020
3 * This program uses a list
4*/
5
6using System;
7using System.Collections.Generic;
8
9/*
10 * The Program class
11*/
12class Program {
13 static void Main() {
14 // this function uses a list
15 List<string> words = new List<string>();
16 string temp_word = "Go";
17
18 Console.WriteLine("Please enter 1 word at a time. Enter STOP to end.");
19
20 while (temp_word != "STOP") {
21 Console.Write("Enter a word: ");
22 temp_word = Console.ReadLine();
23 words.Add(temp_word);
24 }
25
26 words.RemoveAt(words.Count - 1); // remove the "STOP" that was added
27 Console.WriteLine();
28
29 Console.WriteLine("Here are the words reversed:");
30 while (words.Count > 0) {
31 Console.WriteLine(words[words.Count - 1]);
32 words.RemoveAt(words.Count - 1);
33 }
34
35 Console.WriteLine("\nDone.");
36 }
37}
1/**
2 * Created by: Mr. Coxall
3 * Created on: Sep 2020
4 * This program uses a list
5 */
6
7package main
8
9import (
10 "container/list"
11 "fmt"
12)
13
14func main() {
15 // this function uses a list
16 words := list.New()
17 tempWord := "Go"
18
19 fmt.Println("Please enter 1 word at a time. Enter STOP to end.")
20
21 for tempWord != "STOP" {
22 fmt.Print("Enter a word: ")
23 fmt.Scan(&tempWord)
24 words.PushBack(tempWord)
25 }
26
27 words.Remove(words.Back()) // remove the "STOP" that was added
28 fmt.Println()
29
30 fmt.Println("Here are the words reversed:")
31 for singleWord := words.Back(); singleWord != nil; singleWord = singleWord.Prev() {
32 fmt.Println(singleWord.Value)
33 }
34
35 fmt.Println("\nDone.")
36}
1/*
2 * This program uses a list
3 *
4 * @author Mr Coxall
5 * @version 1.0
6 * @since 2020-09-01
7 */
8
9import java.util.Scanner;
10import java.util.ArrayList;
11import java.util.List;
12
13public class Main {
14 public static void main(String[] args) {
15 // this function uses a list
16 List<String> words = new ArrayList<>();
17 String tempWord = "Go";
18
19 System.out.println("Please enter 1 word at a time. Enter STOP to end.");
20
21 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
22 while (!tempWord.equalsIgnoreCase("STOP")) {
23 System.out.print("Enter a word: ");
24 tempWord = scanner.nextLine();
25 words.add(tempWord);
26 }
27
28 words.remove(words.size() - 1); // remove the "STOP" that was added
29 System.out.println();
30
31 System.out.println("Here are the words reversed:");
32 for (int loopCounter = words.size() - 1; loopCounter >= 0; loopCounter--) {
33 System.out.println(words.get(loopCounter));
34 }
35
36 System.out.println("\nDone.");
37 }
38}
1/* Created by: Mr. Coxall
2 * Created on: Sep 2020
3 * This program uses a list
4 */
5
6const prompt = require("prompt-sync")()
7
8// input
9const words = [];
10let tempWord = 'Go';
11
12console.log('Please enter 1 word at a time. Enter STOP to end.');
13
14while (tempWord.toUpperCase() !== 'STOP') {
15 tempWord = prompt('Enter a word: ');
16 words.push(tempWord);
17}
18
19words.pop(); // remove the "STOP" that was added
20console.log();
21
22console.log('Here are the words reversed:');
23for (let loopCounter = words.length - 1; loopCounter >= 0; loopCounter--) {
24 console.log(words[loopCounter]);
25}
26
27console.log("\nDone.")
1#!/usr/bin/env python3
2"""
3Created by: Mr. Coxall
4Created on: Sep 2020
5This module program uses a list
6"""
7
8
9def main() -> None:
10 """The main() this function uses a list, returns None."""
11
12 # input
13 words = []
14 temp_word = "Go"
15
16 # input
17 print("Please enter 1 word at a time. Enter STOP to end.")
18
19 while temp_word.upper() != "STOP":
20 temp_word = input("Enter a word: ")
21 words.append(temp_word)
22
23 words.pop() # remove the "Stop" that was added
24 print("")
25
26 print("Here are the words reversed:")
27 for _ in range(0, len(words)):
28 print(words.pop())
29
30 print("\nDone.")
31
32
33if __name__ == "__main__":
34 main()
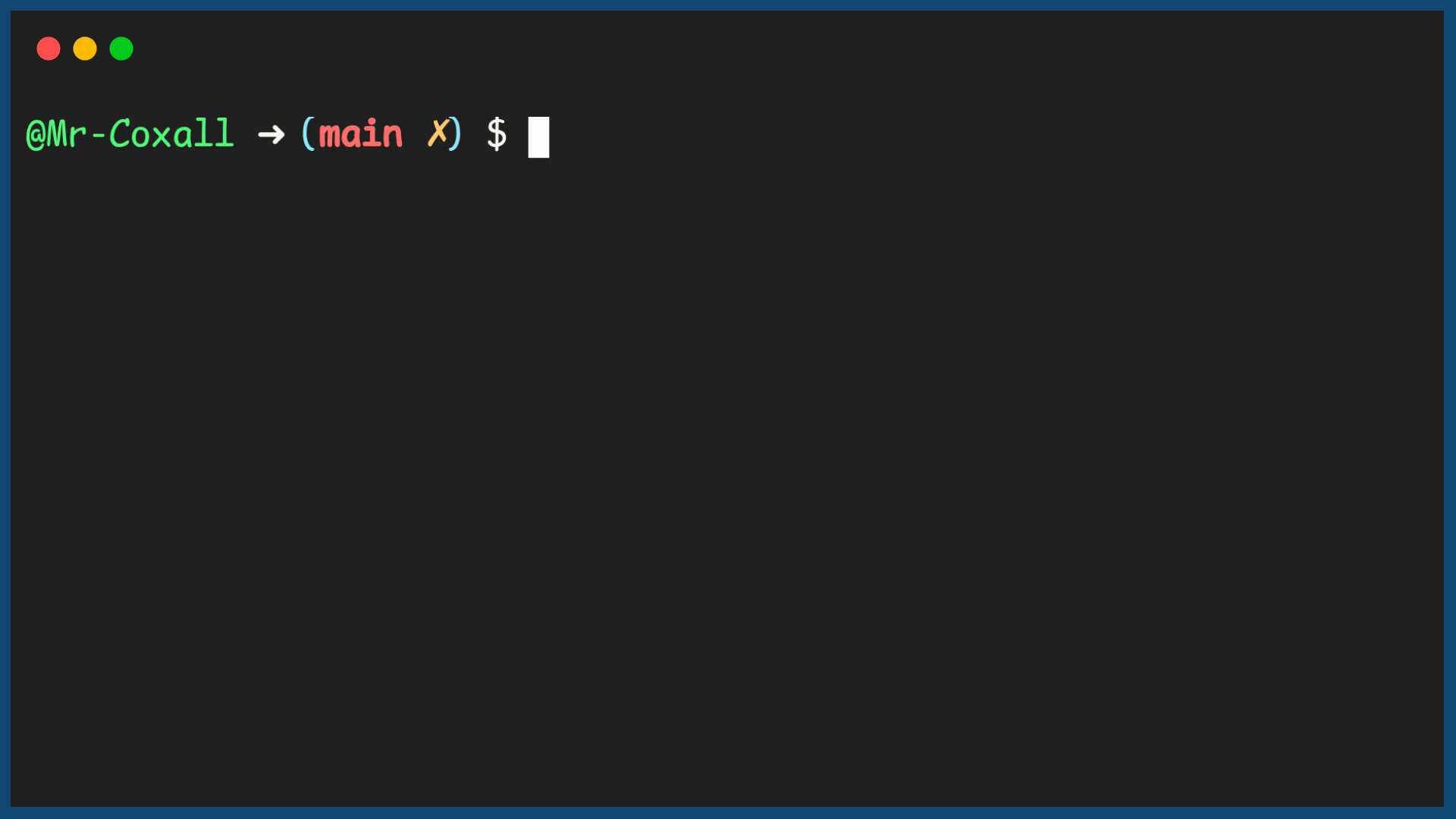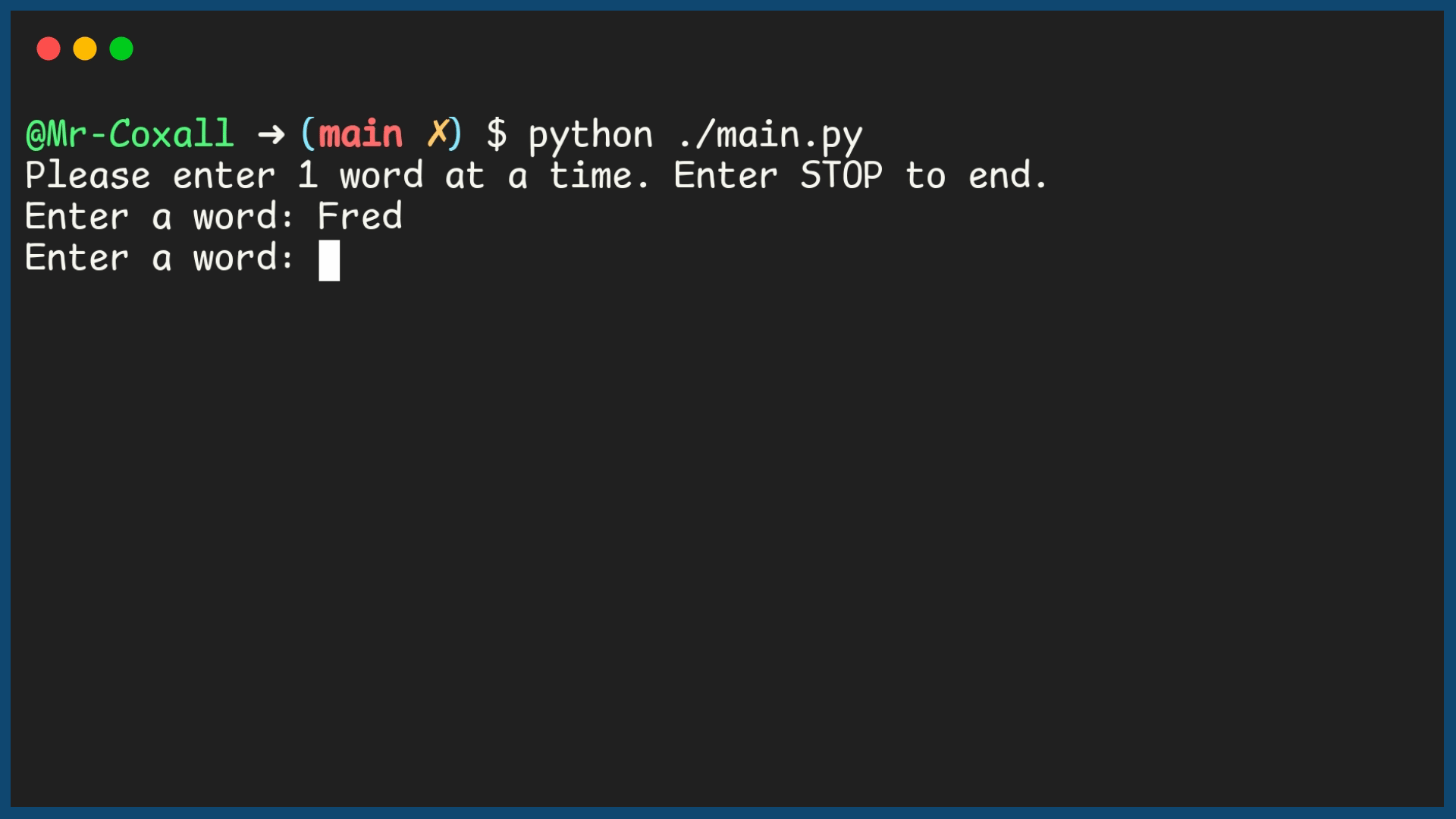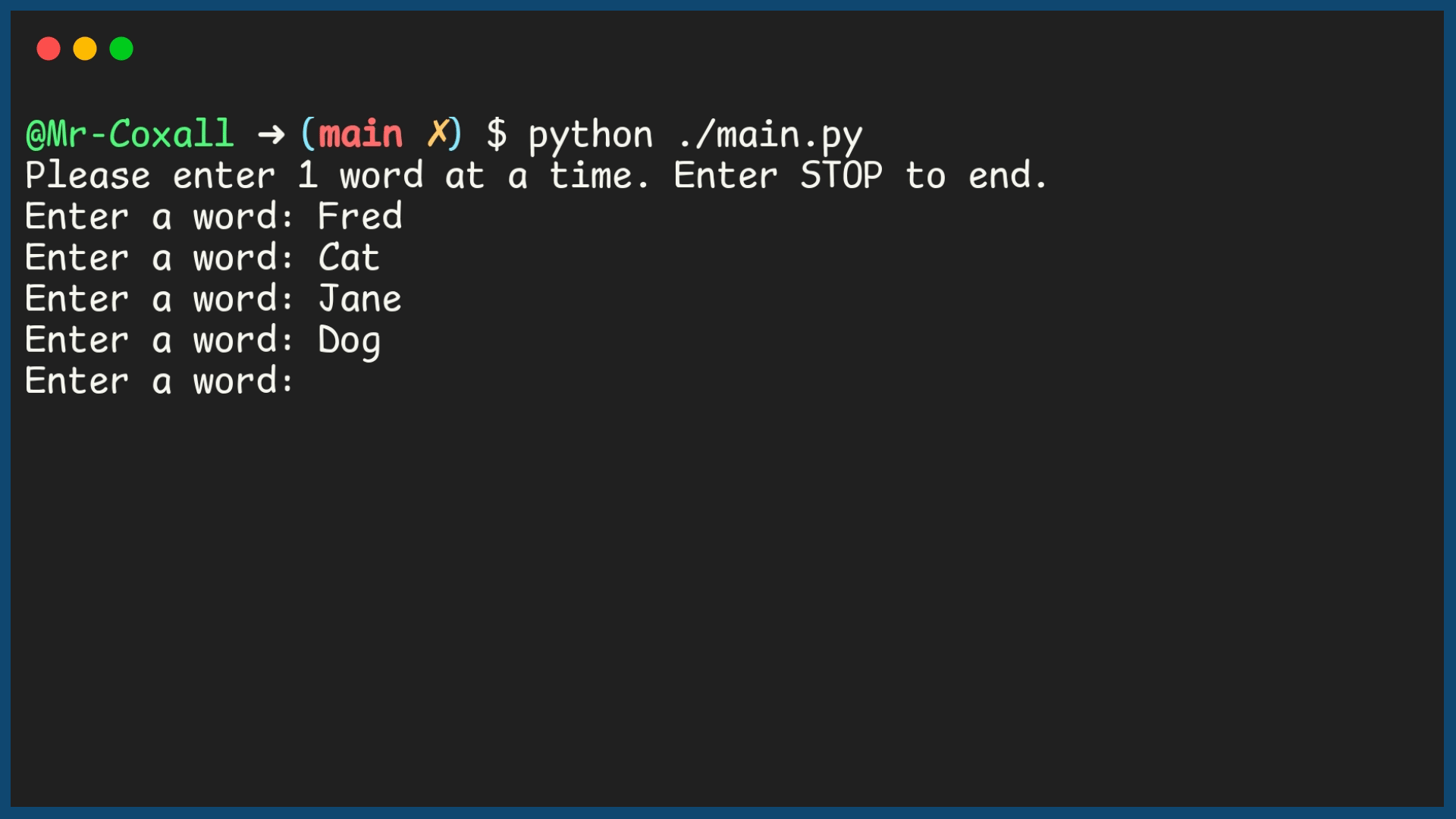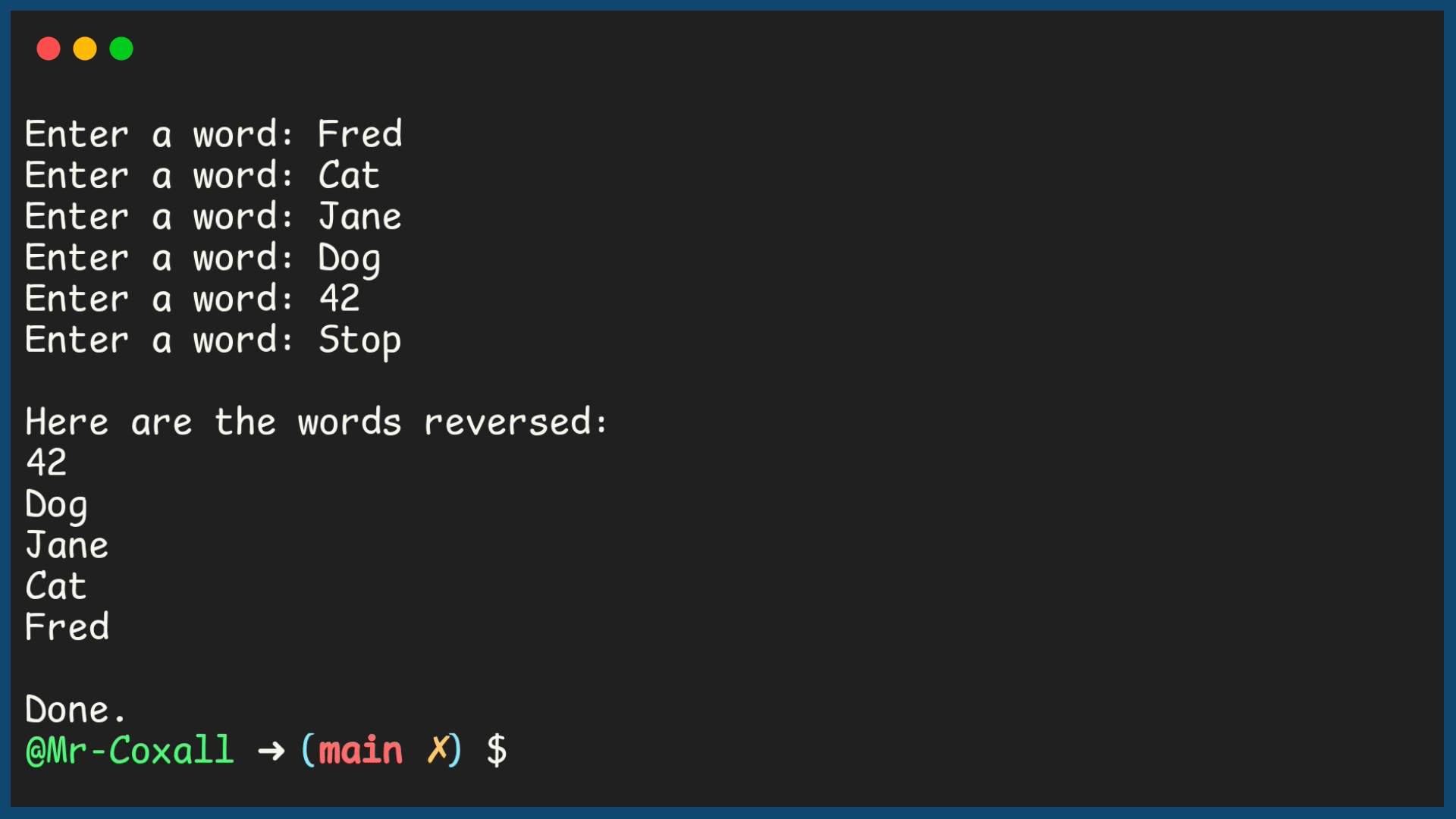
Example Output