2D Arrays
All the arrays that we have used thus far have been to represent a collection of information. This is a very powerful tool and can save the programmer a lot of time and confusion when dealing with items that are somehow related to each other. Not all things can be represented with a single collection though. Several times we use a grid or spreadsheet to keep information in rows and columns. This matrix of information can not be represented in a single array. In these situations we represent our data with a 2-dimensional (or multi-dimensional array ).
A 2-D array can just be thought of an array of arrays.
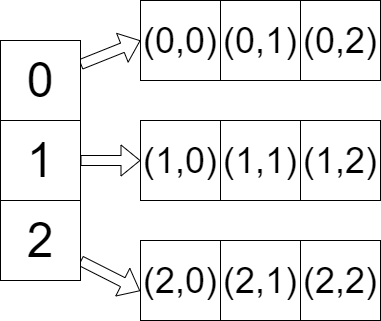
We represent a given element with 2 indices now, instead of 1 when we had a single dimension. Unlike in math class where you used the Cartesian plane, and moved in the X direction and then the Y direction,
in computer science you move up and down in the rows first and then across to the column position. Thus if we want to refer to the element in the above array that has a value of 8, we would say, studentMarks(2, 1).
There are many applications of 2-D arrays, like a game board (tic-tac-toe), adventure games and business applications like spreadsheets.
Code for Creating and using a 2D Array
1// Copyright (c) 2020 Mr. Coxall All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program uses a 2D array as a parameter
6
7#include <stdio.h>
8#include <stdlib.h>
9#include <time.h>
10
11// in C you must pass in the size of the 2D array to a function, first
12int sumOfNumbers(int rows, int columns, int arrayOfNumbers[rows][columns]) {
13 // this function adds up all of the numbers in a 2D array
14
15 int total = 0;
16
17 // loop through 2D array and add all numbers together
18 for (int rowCounter = 0; rowCounter < rows; rowCounter++) {
19 for (int columnCounter = 0; columnCounter < columns; columnCounter++) {
20 total += arrayOfNumbers[rowCounter][columnCounter];
21 }
22 }
23
24 return total;
25}
26
27int main() {
28 // this function uses a 2D array
29 const int rows = 7;
30 const int columns = 5;
31 int number2DArray[rows][columns];
32 int seed = time(NULL);
33
34 // input
35 srand(seed);
36 // Generate random numbers and populate the 2D array
37 for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++) {
38 for (int column = 0; column < columns; column++) {
39 int aRandomNumber = rand() % 9;
40 number2DArray[row][column] = aRandomNumber;
41 printf("%d ", aRandomNumber);
42 }
43 printf("\n");
44 }
45 printf("\n");
46
47 // call function
48 int sumNumbers = sumOfNumbers(rows, columns, number2DArray);
49
50 // output
51 printf("The sum of all the numbers is: %d\n", sumNumbers);
52
53 printf("\nDone.\n");
54 return 0;
55}
1// Copyright (c) 2020 Mr. Coxall All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program uses a 2D array as a parameter
6
7#include <iostream>
8#include <cstdlib>
9#include <ctime>
10
11
12// In C++, a 2D array is passed by reference to a function
13// (template is used to find the length of the array)
14template <int rows, int cols>
15int sumOfNumbers(int (&passedIn2DArray)[rows][cols]) {
16 // this function adds up all of the numbers in a 2D array
17
18 int total = 0;
19 int counter = 0;
20
21 //adding up all of the numbers in a 2D array
22 for (int rowCounter = 0; rowCounter < rows; rowCounter++) {
23 for (int columnCounter = 0; columnCounter < cols; columnCounter++) {
24 total += passedIn2DArray[rowCounter][columnCounter];
25 }
26 }
27
28 return total;
29}
30
31int main() {
32 // this function uses a 2D array
33 const int rows = 3;
34 const int columns = 5;
35 int a2DArray[rows][columns];
36 int aSingleRandomNumber = 0;
37 int sum = 0;
38
39 srand(time(NULL));
40
41 // input
42
43 // So, ...
44 // In C++ you can't define array's size using variable.
45 // this is why you see const int rows = 2; above,
46 // so the size of the array can never change
47
48 for (int rowElement = 0; rowElement < rows; rowElement++) {
49 for (int columnElement = 0; columnElement < columns; columnElement++) {
50 aSingleRandomNumber = (rand() % 9) + 1;
51 a2DArray[rowElement][columnElement] = aSingleRandomNumber;
52 std::cout << aSingleRandomNumber << " ";
53 }
54 std::cout << std::endl;
55 }
56
57 // call functions
58 sum = sumOfNumbers(a2DArray);
59
60 // output
61 std::cout << "The sum of all the numbers is: " << sum << std::endl;
62
63 std::cout << "\nDone." << std::endl;
64 return 0;
65}
1// Copyright (c) 2020 St. Mother Teresa HS All rights reserved.
2//
3// Created by: Mr. Coxall
4// Created on: Sep 2020
5// This program uses a 2D array
6
7using System;
8
9class Program
10{
11 static int SumOfNumbers(int[,] arrayOfNumbers)
12 {
13 // This function adds up all of the numbers in a 2D array
14
15 int total = 0;
16 int rows = arrayOfNumbers.GetLength(0);
17 int columns = arrayOfNumbers.GetLength(1);
18
19 // Loop through 2D array and add all numbers together
20 for (int rowCounter = 0; rowCounter < rows; rowCounter++) {
21 for (int columnCounter = 0; columnCounter < columns; columnCounter++) {
22 total += arrayOfNumbers[rowCounter, columnCounter];
23 }
24 }
25
26 return total;
27 }
28
29 static void Main()
30 {
31 // This function uses a 2D array
32 const int rows = 7;
33 const int columns = 5;
34 int[,] number2DArray = new int[rows, columns];
35 Random random = new Random();
36
37 // Generate random numbers and populate the 2D array
38 for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++)
39 {
40 for (int column = 0; column < columns; column++)
41 {
42 int aRandomNumber = random.Next(10);
43 number2DArray[row, column] = aRandomNumber;
44 Console.Write($"{aRandomNumber} ");
45 }
46 Console.WriteLine();
47 }
48 Console.WriteLine();
49
50 // Call function
51 int sumNumbers = SumOfNumbers(number2DArray);
52
53 // Output
54 Console.WriteLine($"The sum of all the numbers is: {sumNumbers}");
55
56 Console.WriteLine("\nDone.");
57 }
58}
1#!/usr/bin/env python3
2"""
3Created by: Mr. Coxall
4Created on: Sep 2020
5This module uses an array as a parameter
6"""
7
8
9import random
10from typing import List
11
12
13# in python an array is passed by reference to a function
14def sum_of_numbers(array_of_numbers: List[List[int]]) -> int:
15 """The sum_of_numbers() function calculates the sum of numbers in a 2D list, returns the sum as int."""
16
17 total = 0
18
19 for row_value in array_of_numbers:
20 for single_value in row_value:
21 total += single_value
22
23 return total
24
25
26def main() -> None:
27 """The main() function just calls other functions, returns None."""
28
29 a_2d_list = []
30 sum_answer = 0
31
32 # input
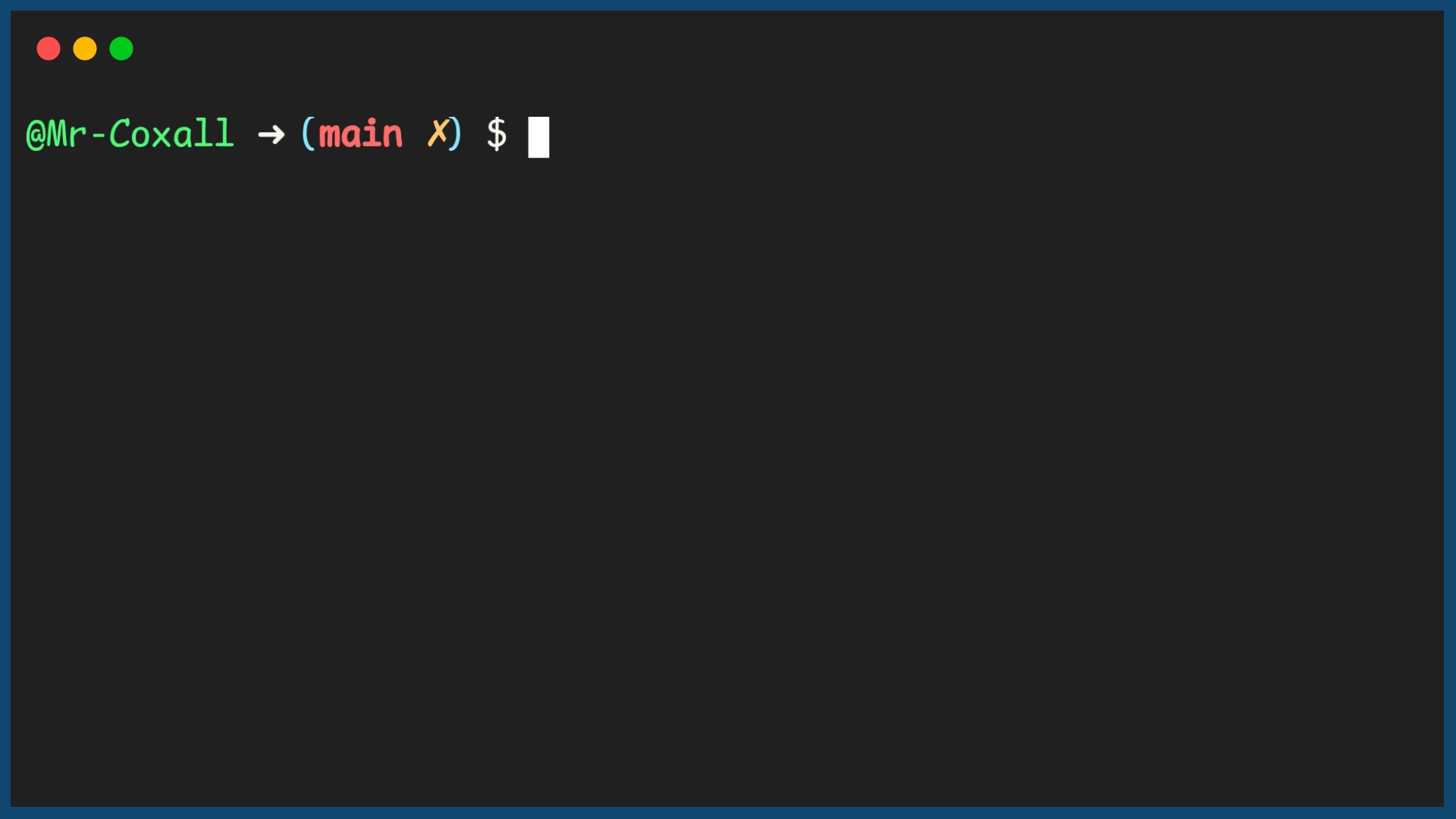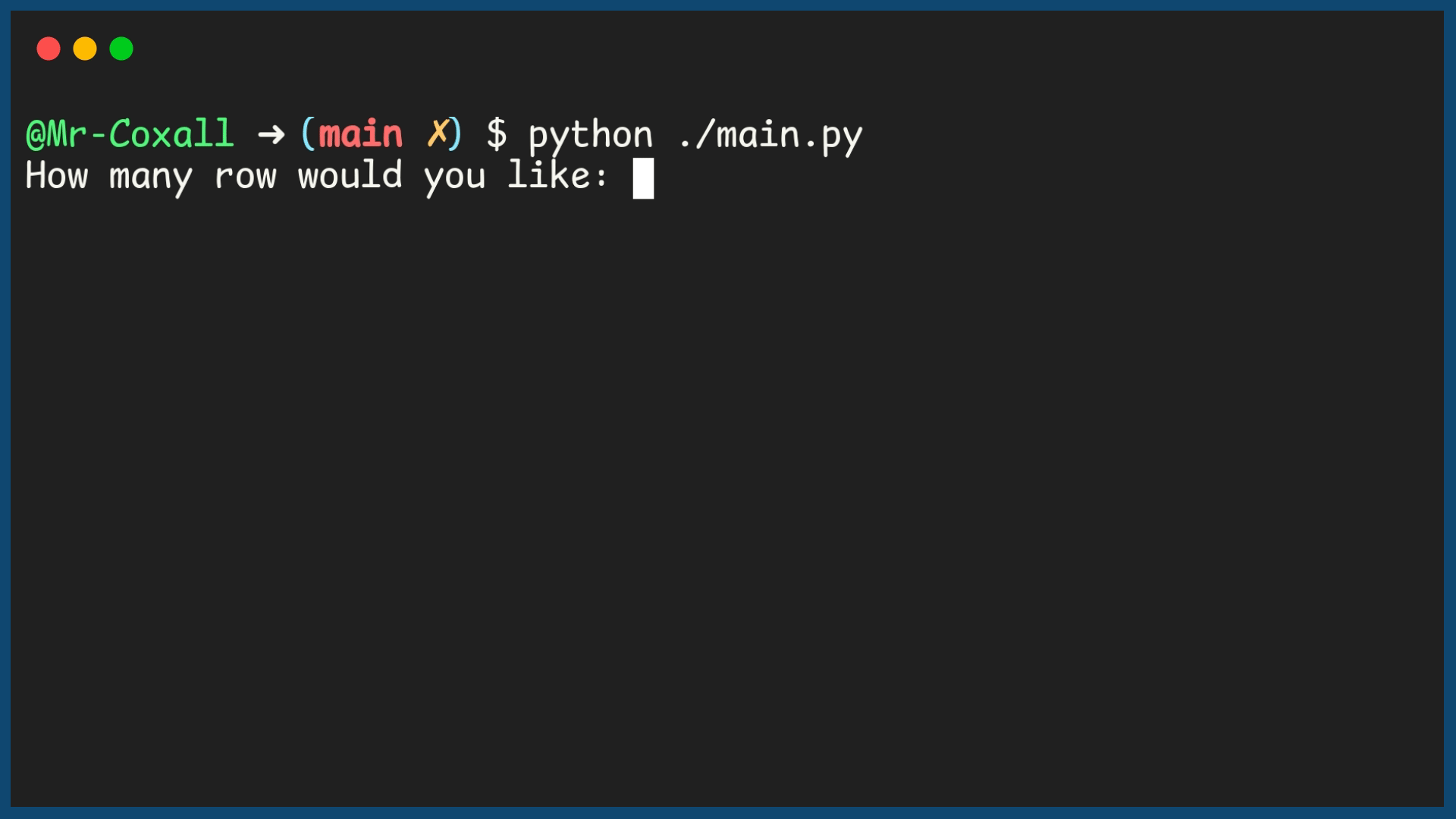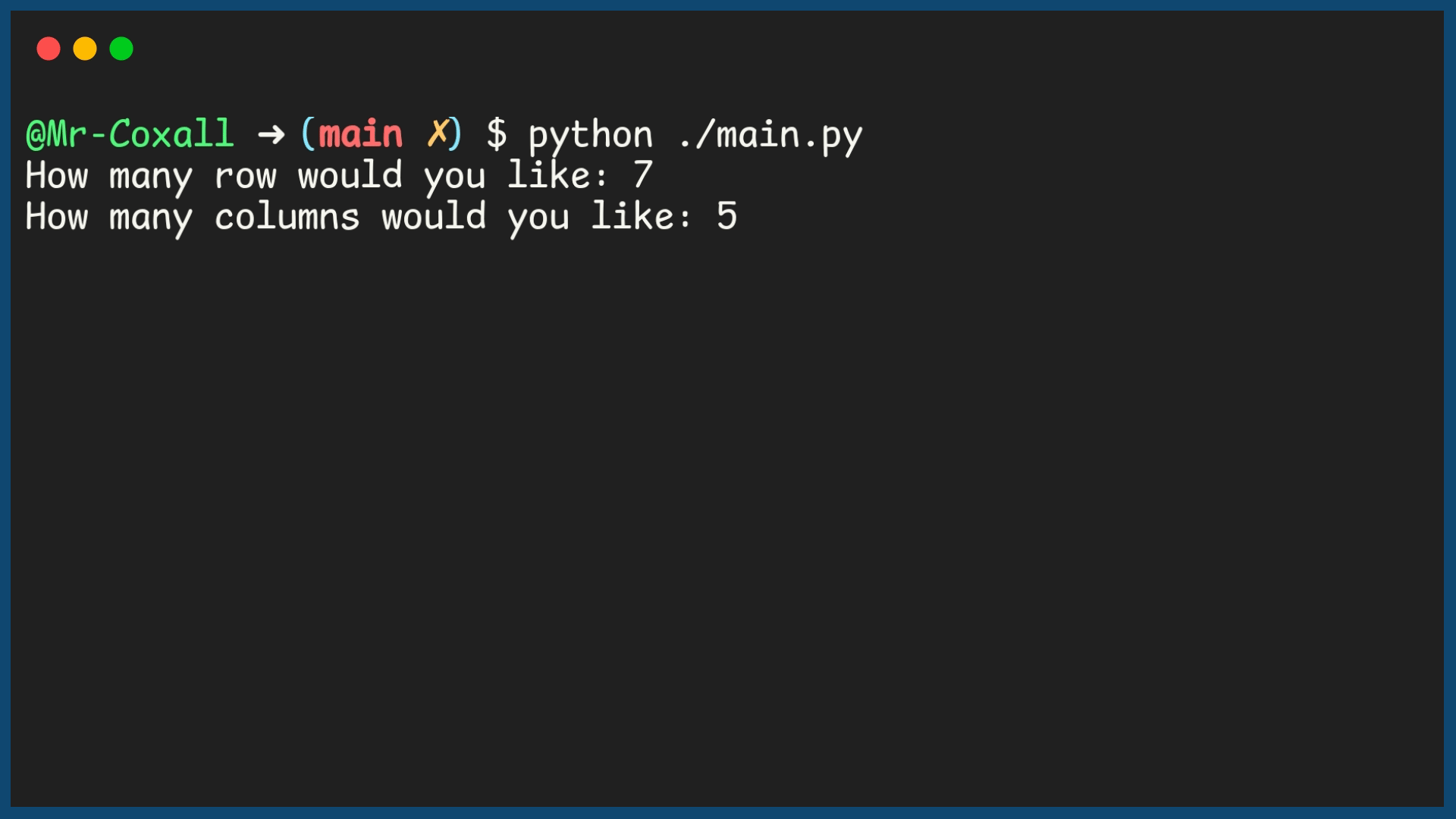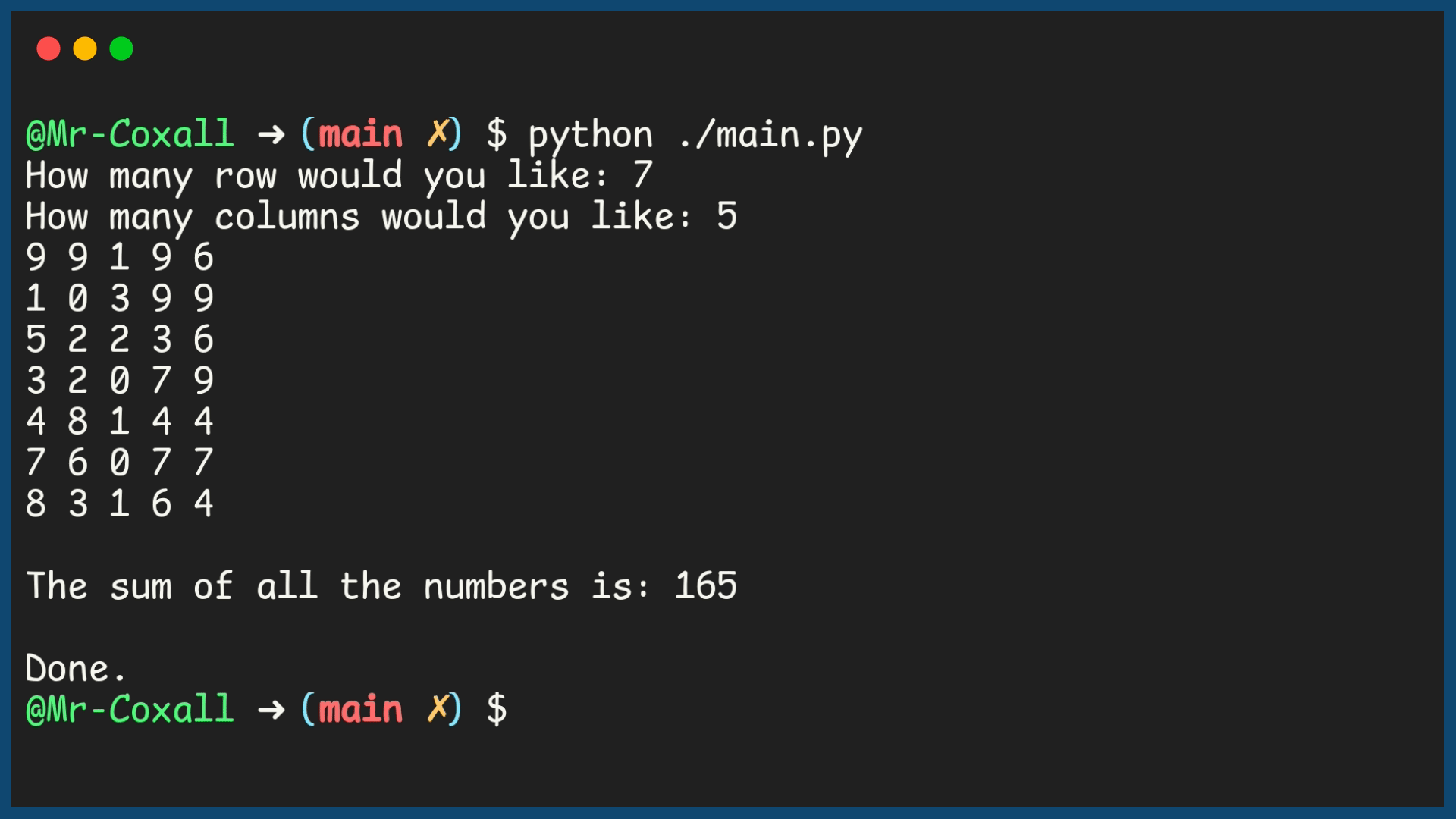
33 rows = int(input("How many row would you like: "))
34 columns = int(input("How many columns would you like: "))
35
36 for _ in range(0, rows):
37 temp_column = []
38 for _ in range(0, columns):
39 a_random_number = random.randint(0, 9)
40 temp_column.append(a_random_number)
41 print(f"{a_random_number} ", end="")
42 a_2d_list.append(temp_column)
43 print("")
44
45 sum_answer = sum_of_numbers(a_2d_list)
46
47 # output
48 print(f"\nThe sum of all the numbers is: {sum_answer}")
49
50 print("\nDone.")
51
52
53if __name__ == "__main__":
54 main()
Example Output